画像をダウンロード sinus bradycardia rhythm 6 second strip 231918
Chapter 5 Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 51 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings and determining the presence of dysrhythmias 52 Describe the criteria used for classification of dysrhythmias, including rhythm, rate, P wave configuration, PR interval measurement, and QRS duration measurementRationale 1 Normal sinus rhythm is defined as regular rhythm with a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute The PR and QRS measurements are normal, 012 to 0 second and 006 to 010 second respectively Rationale 2 The rhythm is regular, which is not a characteristic of sick sinus syndrome Rationale 3 The rate is too fast for sinus bradycardiaSinus bradycardia is discussed including the ECG criteria, causes and symptoms when a part of sick sinus syndrome (SSS)
Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx
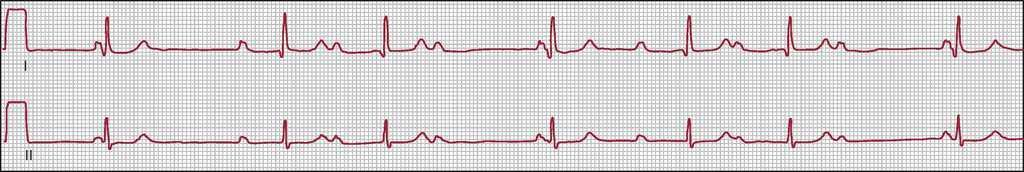
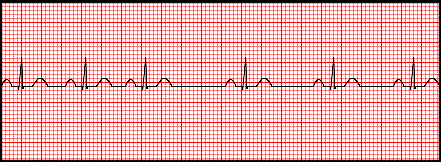
Sinus bradycardia rhythm 6 second strip
Sinus bradycardia rhythm 6 second strip-Sinus Rhythms are aptly named due to the locus of stimulation being the SA (sinoatrial) node With Sinus Bradycardia the locus of stimulation is the same as normal sinus rhythm, just now the rate will be less than 60 bpm Recall that "brady" means slow The only difference between sinus bradycardia and normal sinus rhythm is the rate• Cycles/6 second strip 10 = Rate • When there are 10 large squares between similar waves, the rate is 30/minute Sinus Rhythm origin is the SA Node ("Sinus Node"), normal sinus rate is 60 to 100/minute • Rate more than 100/min = Sinus Tachycardia (page 68) • Rate less than 60/min = Sinus Bradycardia (page 67)




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx
2906 · Sinus Tachycardia Originates from the SA node Atrial and ventricular rates are the same and are between 100 and 150 beats per minute Increased heart rate could be normal response to recent exercise Sinus tachycardia can cause low cardiac output Patient may complain of heart fluttering or palpitations Criteria for rhythm, P wave morphology, PR interval, and QRS duration and morphology are the same as in sinus rhythm and sinus bradycardiaNote The rate of a Normal Sinus Rhythm is beats per minute;The following rhythm strips are for your practice We suggest you practice with these prior to taking the post test (All strips are sixsecond strips unless otherwise indicated) Rhythm Strip #1 ECG Criteria Heart rate
· This rhythm strip tracing shows an atrial tachyarrhythmia (atrial flutter/tachycardia) that suddenly terminates The tachycardia is followed by a 34second pause and then sinus bradycardia The combination of a tachycardia that is suddenly followed by a bradycardia is characteristic of tachybrady syndromeAssume each strip is a 6 second strip Passing is 80% 1 Identify the following rhythm a Asystole b Ventricular fibrillation c Atrial fibrillation d Torsade de pointes 2 What is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?Rate and Rhythm Sinus Bradycardia and Sinus Tachycardia Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device Up next
Basic Dysrhythmias Sinus Arrhythmias Basic Rhythm Strip Interpretation6 Cardiac physiology 10 The P wave 13 The PR interval 15 The QRS complex 18 The ST segment The T wave 22 Determining the rate 24 Myocardial Infarction 27 Sinus Rhythm (SR) 29 Sinus Bradycardia (SB) 31 Sinus Tachycardia (ST) 33 Atrial Tachycardia 34 Atrial Fibrillation (AF) 36 Atrial Flutter 38 Junctional Escape RhythmBradycardia sinus bradycardia is seen in a skipped rhythm, Causes are second and third degree AV block, sinoatrial block and arrest termed sinus node dysfunction enabling quicker appraisal of heart rate based on a 6second strip the procedure is as follows Obtain a printed strip of sufficient length, covering more than 6 seconds,



Bradyarrhythmias And Conduction Blocks Revista Espanola De Cardiologia



Cardiac Arrhythmias And Conduction Disturbances Musculoskeletal Key
To determine if the atrial rate is regular or irregular, measure the distance between two consecutive PP intervals Use a point from one P wave to the same point on the next P wave · basic rhythm strip review 1 rhythm strip review 2 measuring intervals 3 measuring intervals 4 sinus rhythms 5 normal sinus rhythm 6 sinus arrhythmia 7 sinus tachycardia 8 sinus bradycardia 9 sinus pause 10 sinus arrest 11 atrial rhythms 123012 · We cannot use the guestimation method here, because this is not a 6second strip In fact, it's about a 3second strip, so that would put us around 60bpm which would just be normal sinus rhythm so you can see why this method is not as accurate, and on a test, you'd have gotten this question wrong if you used that method



6 Interpretation Of An Ekg Strip Ppt Download



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx
C) Sinus bradycardirrest 2 Identify on rrest 3 Systematically evaluate each rhythm for the following criteria a) Rate, b) Rhythm Regular/irregular,Identify on rrest 3 Systematically evaluate each rhythm for the following criteria a) Rate, b) Rhythm Regular/irregular,Sinus bradycardia ECG, causes & management Definition of sinus bradycardia Sinus bradycardia fulfills the criteria for sinus rhythm but the heart rate is slower than 50 beats per minute ECG criteria follows Regular rhythm with ventricular rate slower than 50 beats per minute Pwaves with constant morphology preceding every QRS complex



Ecg




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx
0118 · Sinus rhythm refers to the pace of your heart beat that's set by the sinus node, your body's natural pacemaker A normal sinus rhythm means your heart rate is within a normal range · Even people who are physically fit can experience sinus bradycardia Bradycardia is often indicative of low blood pressure, pulmonary edema and congestion, abnormal rhythm, discomfort in the chest, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and/or confusion On the other hand, symptomatic bradycardia should be attended to with the ACLS SurveyHowever, from a cardiologist or EP perspective, this is coarse atrial fibrillation (pseudo flutter waves changing morphology and rate) 32 Sinus Tachycardia



Www Upstate Edu Hr Document Rhythmstest Pdf



Utmc Utoledo Edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Basic ekg refresher Pdf
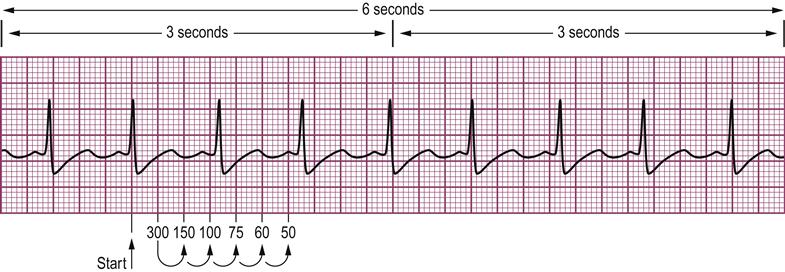
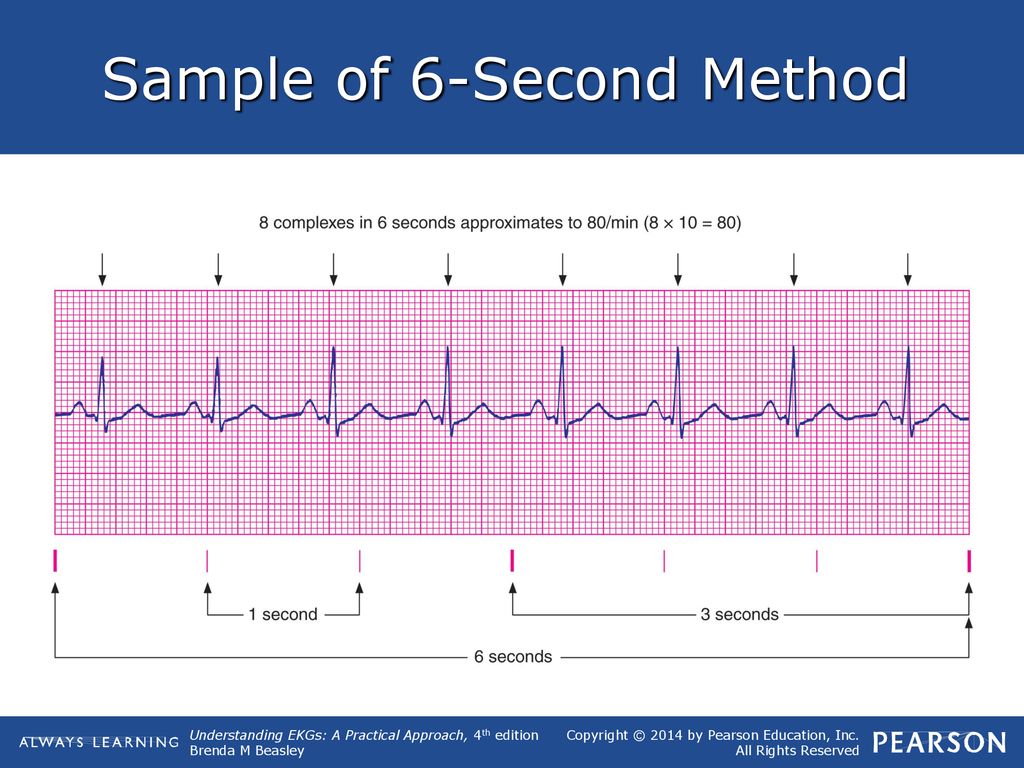
Sinus bradycardia is characterized by sinus rhythm with heart rates below normal for age (see Fig 165) Slow heart rates can be observed during sleep or at times of high vagal tone When there is significant sinus bradycardia, a slow junctional escape rhythm or a slow atrial rhythm originating from an ectopic focus can be presentWhen assessing the rhythm strip, the nurse takes care first to identify the underlying rhythm (eg, sinus rhythm, sinus arrhythmia) Then the PR interval is assessed for the possibility of an AV block AV blocks occur when the conduction of the impulse through the AV0807 · A 6second strip is made up of 30 big boxes Each big block is 02 seconds in duration, so 5 big blocks is equal 1 second in total duration (2 x 5 = 1), meaning you would need a total of 30 big boxes to make a 6second strip Once you know you are dealing with a 6 second strip, you count the number of QRS complexes within those 6 seconds and multiply by 10 For example, if we count 5 QRS complexes within a 6 second strip,




Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet




Basic Ekg And Rhythm Interpretation Symposia The Crudem Foundation
Atrial rate (#P waves in 6second strip)*(10) Ventricular rate (#QRS complexes waves in 6second strip)*(10)An ECG rhythm strip shows a ventricular rate of 128, a regular rhythm, a PR interval of 016 second, a QRS duration of 008, and one upright P wave before each QRS This rhythm29 Accellerated Junctional Rhythm (heart rate is 80) 30 Sinus Bradycardia with 1st degree AV block (PR 022 seconds) HR=50 31 Atrial flutter with varying conduction (saw tooth baseline);



Arrhythmia Recognition The Art Of Interpretation




Practice Test Only Dysrhythmia Interpretation Therapeutic Modalities Pdf Free Download
Bradycardia is the most common feature of sick sinus syndrome Very few patients, however, will actually experience symptoms unless their heart rate drops to Identify on a 6second strip the following rhythms a) Sinus rhythm Sinus bradycardia happens when the sinus node does not send enough electrical impulses to the heart, resulting in a heart rate that is lower than 60 BPMThe 6 second method Denotes a 6 second interval on EKG strip Strip is marked by 3 or 6 second tick marks on the top or bottom of the graph paper Count the number of QRS complexes occurring within the 6 second interval, and then multiply that number by 10 Using rate determination chart More accurate calculation of HRThe normal ST segment is flat, isoelectric Could be indicative of some ischemia or an electrolyte disorder




Practice Test Only Dysrhythmia Interpretation Therapeutic Modalities Pdf Free Download




Rspt 2325 Cardiopulmonary Diagnostics Unit 1 Basic Ekg
Sinus rhythm, bradycardia and tachycardia · Sinus Bradycardia The rhythm is regular There is one upright P wave associated with each QRS complex The PR interval falls within normal range There are no ectopic beats The rate is < 60 beats/min What do you notice about the ST segment?Step Two Determine the Rhythm Is the rhythm is regular or irregular?




Practice Rhythm Strip 1




Ecg Quiz Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia Arvd Ashman Phenomenon Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Atrial Tachycardia Atrioventricular Block Atrioventricular Dissociation Atrioventricular Nodal
· Bradycardia is defined as a heart rate slower than 60 beats per minute Sinus bradycardia is a type of slow heartbeat that originates from the sinus node of your heart Your sinusSinus Rhythms Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus Arrhythmia Sinus Arrest or Pause Sinus Tachycardia Sinus Bradycardia Atrial Rhythms Premature Atrial Contractions (PAC's) Wandering Atrial Pacemaker (WAP) Atrial Tachycardia Atrial measure P wave to P wave across a 6 second strip and note if the P waves are equally spaced (regular · A rhythm strip is at least a 6second tracing printed out on graph paper which shows activity from one or two leads Leads are "views" of the heart There are 12 leads that are traditionally obtained with a 12lead EKG, but most portable and bedside monitors only monitor 35 leads
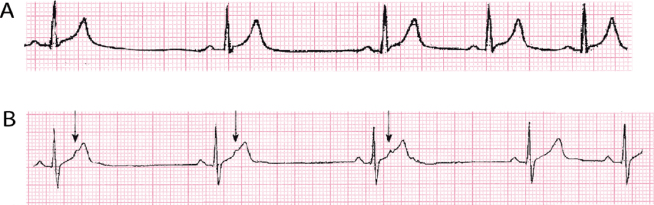



13 The Ecg Patterns Of Passive Arrhythmias Thoracic Key




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx
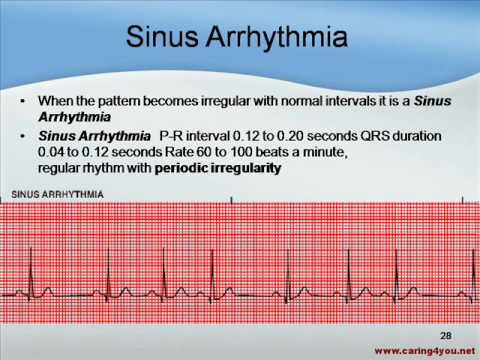
· RHYTHM ECG rhythm characterized by a usual rate of anywhere between 6099 bpm, every P wave must be followed by a QRS and every QRS is preceded by P wave Normal duration of PR interval is 35 small squares The P wave is upright in leads I and II Normal Sinus Rhythm 36 Sinus Bradycardia RHYTHM Rate < 60bpm, otherwise normal 37A patient admitted with a new diagnosis of hypertension demonstrates sinus bradycardia with a heart rate of 52 bpm on the electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor The nurse assesses the patient and determines if the patient is asymptomaticRhythm Strip #3 Heart rate 40 Rhythm Regular P waves One present for each QRS PR interval 12 QRS width 08 Interpretation Sinus bradycardia with (unifocal) ventricular bigeminy




Acls Symptomatic Bradycardia



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice
SecondDegree Atrioventricular Block (Mobitz II) SinusBrdycrdia Sinus Tachycardia ThirdDegree Atrioventricular Block RHYTHM & M ETIOLOGY CRITERIA OVERVIEW UNIQUE CRITERIA SA PLE STRIS Normal Sinus Rhythm • Normal, None RHY – Regular R – P – Upright PRI – 01 QRS – None, normal rhythm Sinus Tachycardia1401 · So step 6 would be to identify the rhythm and we have sinus bradycardia So let's recap and break it down and look at the characteristics of sinus bradycardia Our rhythm is regular, our heart rate is 5051 beats per minute our P to QRS ratio is 1 to 1 our PR interval in normal and our QRS complex is normal so that gives us sinus bradycardiaSinus bradycardia is a type of slow heartbeat A special group of cells begin the signal to start your heartbeat These cells are in the sinoatrial (SA) node Normally, the SA node fires at about 60 to 100 times per minute at rest In sinus bradycardia, the node fires less than 60 times per minute




How To Calculate The Heart Rate On An Ekg Strip With The Six Second Rule
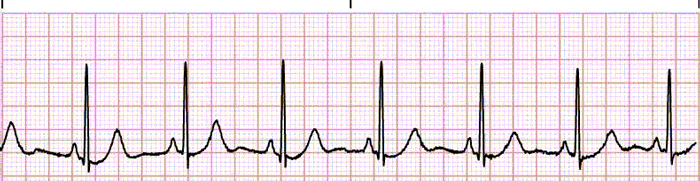



The 6 Steps Method On How To Interpret Electrocardiogram Results Easily Rnspeak
Interpret the strip shown below A Sinus Bradycardia B Atrial Fibrillation with from MED 101 at University of Massachusetts, AmherstDefinition of Sinus Bradycardia Sinus bradycardia is a heart rhythm that originates in the sinus node with a rates less than 60 beats per minute Sinus bradycardia is a common condition in both healthy individuals, particularly athletes It can also occur normally during sleepC) Sinus rhythm at 60 bpm d) Sinus bradycardia A 76yearold man complaining of indigestion a) Junctional bradycardia with STsegment depression and inverted T waves b) Sinus bradycardia with inverted T waves c) Sinus bradycardia with 2nd degree type II d) Junctional bradycardia 21 A 61yearold man with a history of heart failure
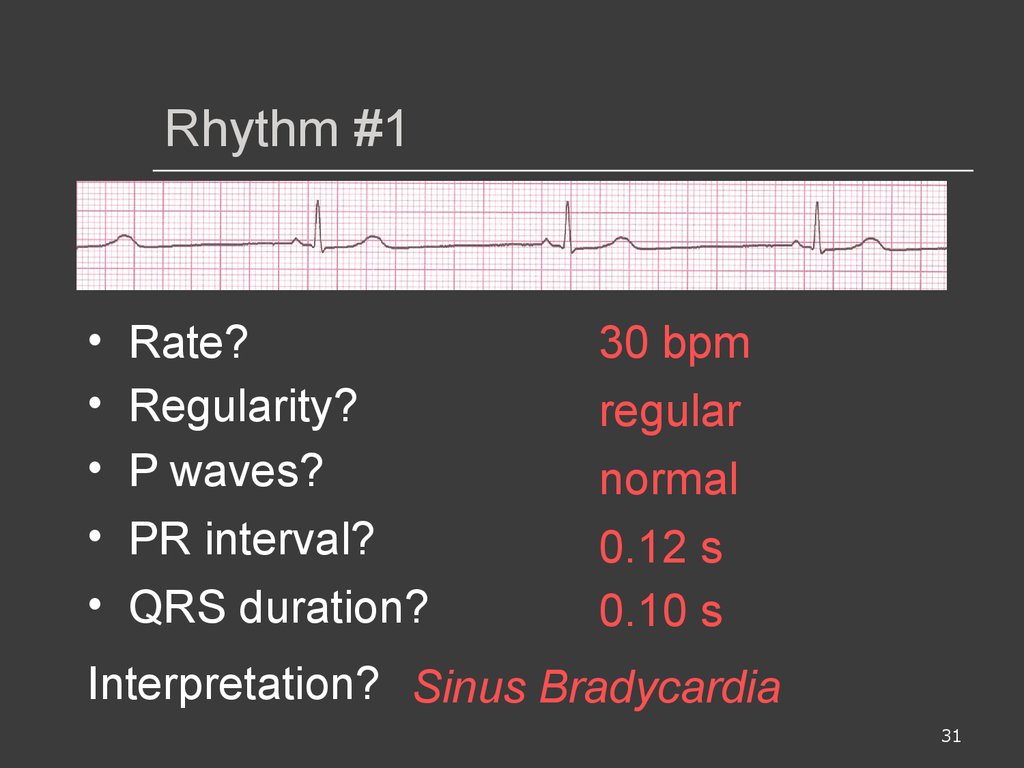



Ecg Interpretations How To Analyze A Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Heart Arrhythmias Diagnosing A Myocardial Infarction Prezentaciya Onlajn




Ecg Learning Center Test
This ECG rhythm is called a) Sinus arrhythmia b) Junctional rhythm c) Junctional bradycardia d) Sinus bradycardia Answer c) Junctional bradycardia Explanation This extremely slow ECG rhythm includes narrow QRS complexes, no P waves and a rate of about 30/minute This rhythm originates from the AV junction Because this rhythm occursA normal heart should have a normal sinus rhythm, this rhythm can be identified by a ventricular rate of bpm, at a regular rate, with a normal PR interval (012 to 0 second) and a normal QRS complex (012 second and less) Sinus bradycardia is another regular rhythm however the ventricular rate is only between 4060 bpm, with a normalSinus tachycardia is recognized on an ECG with a normal upright P wave in lead II preceding every QRS complex, indicating that the pacemaker is coming from the sinus



Utmc Utoledo Edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Basic ekg refresher Pdf




Aclsrhythmtest11 Pdf Cardiac Arrhythmia Cardiology
· Section 1 Supraventricular rhythms Normal sinus rhythm Normal sinus rhythm with a normal U wave Sinus arrhythmia (irregular sinus rhythm) Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Atrial bigeminy Atrial trigeminy Ectopic atrial rhythm Multifocal atrial tachycardia Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response Atrial fibrillation and bundle branch block AtrialA Call the Code team, defibrillate, and administer Magnesium Sulfate B Call MD, review medications



Mark Hammerschmidt Arrythmia Faq




Cardiac Monitoring And The Use Of A Systematic Approach In Interpreting Electrocardiogram Rhythms



Http Www Nwcemss Org Assets 1 System Entry Sinus Rhythms Dysrhythmias F18 Pdf




Ekg Ecg Interpretation Course Ceufast Nursing Continuing Education



Www Upstate Edu Hr Document Rhythmstest Pdf



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn
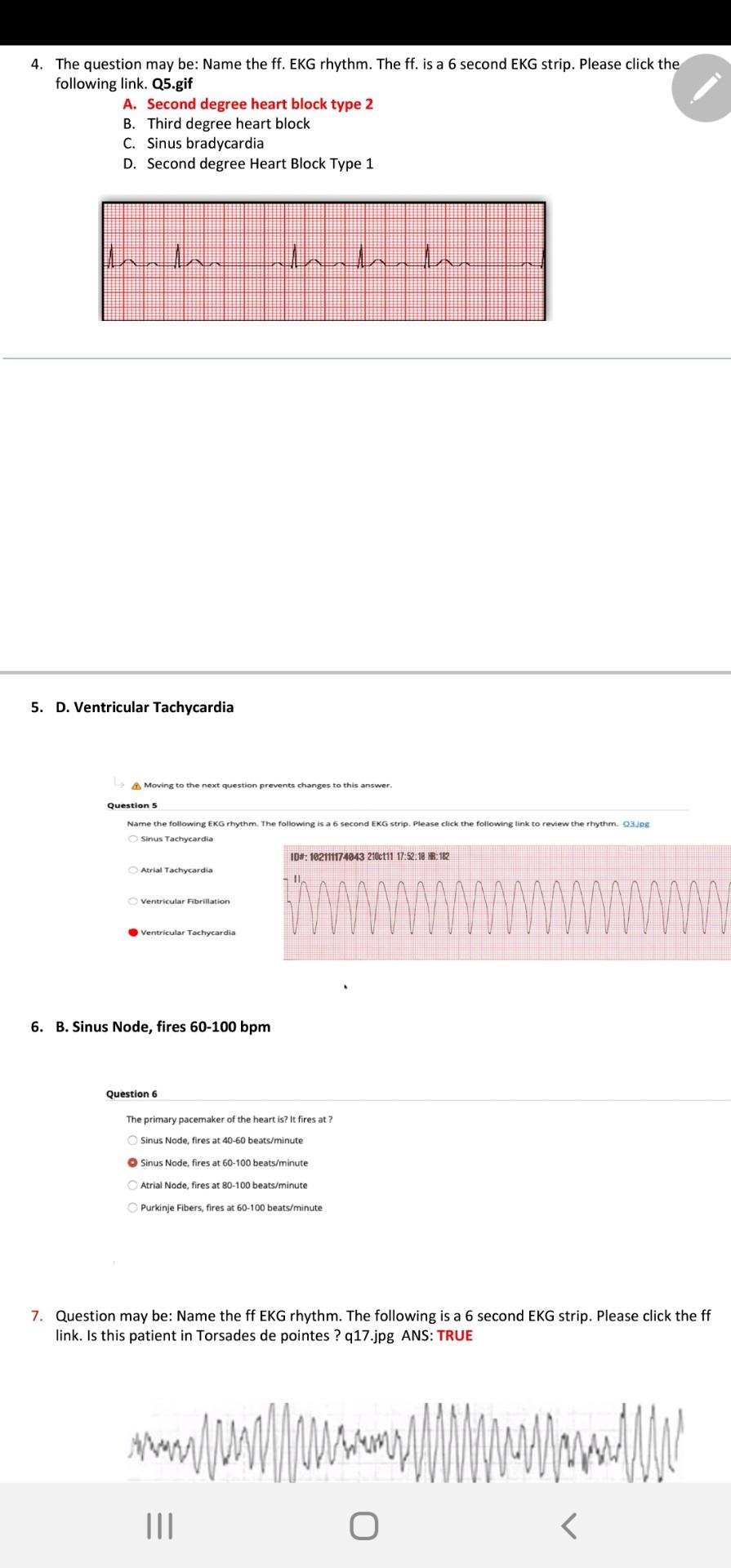



Solved 4 The Question May Be Name The Ff Ekg Rhythm T Chegg Com



Q Tbn And9gctfibdsrfqbvjfprql7q8nbjmy4s3y7vayog7bh Pitxol2skpr Usqp Cau




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn



Med Virginia Edu Emergency Medicine Wp Content Uploads Sites 232 15 10 Introduction To Ecg Rhythms Pdf



Nt Prophecyhealth Com Docs Manuals Foundations Of Ecg Interpretation1 Pdf




Arrhythmias Rn Expert Guides Cardiovascular Care 1st Edition 08



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice



Www Upstate Edu Hr Document Rhythmstest Pdf




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn



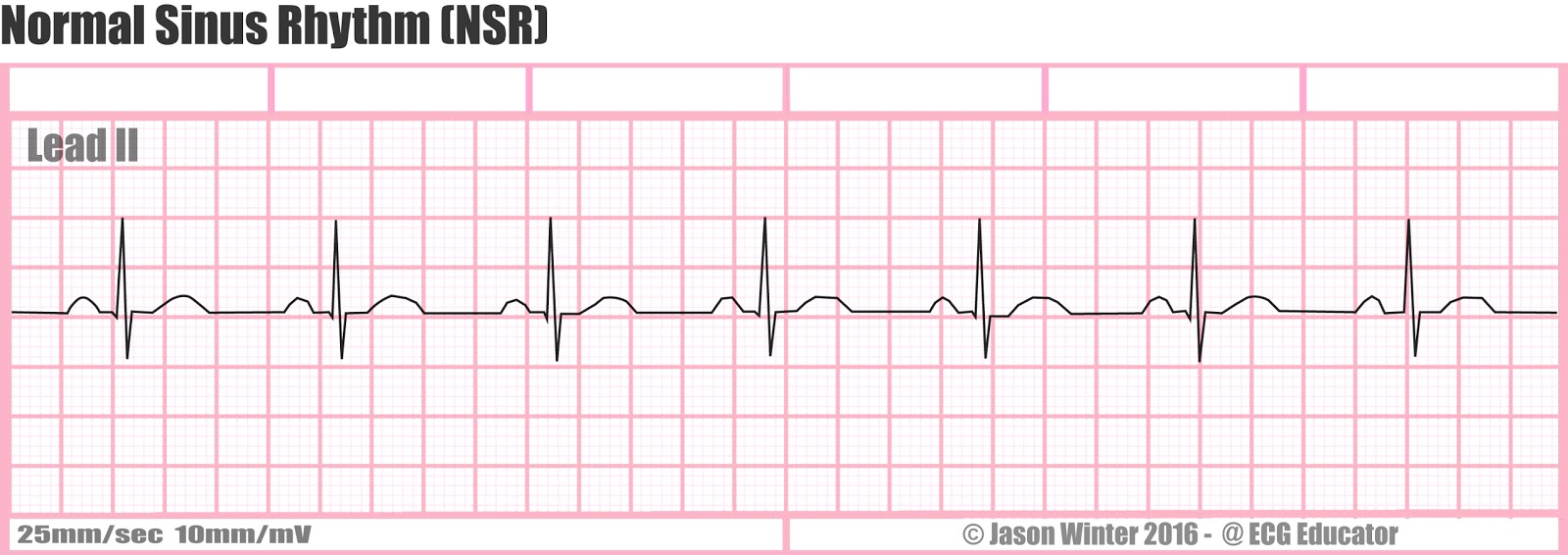
Sinus Rhythm Quiz Quizizz



Ecg A Pictorial Primer




Acls Rhythm Test 2 A 74 Year Old Woman With Chest Pain Blood Pressure 192 90 And Rates Her Pain 9 10 Pdf Free Download




How To Calculate The Heart Rate On An Ekg Strip With The Six Second Rule



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf



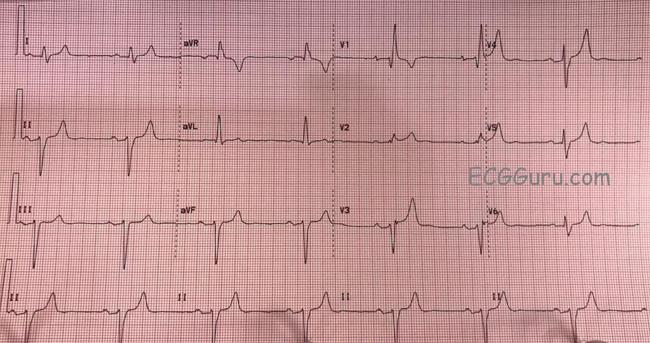
How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx



Med Virginia Edu Emergency Medicine Wp Content Uploads Sites 232 15 10 Introduction To Ecg Rhythms Pdf



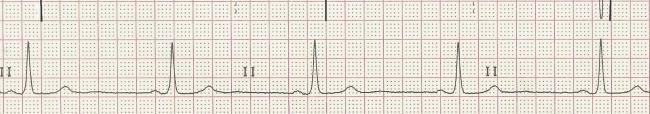
Sinus Bradycardia Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Www Skillstat Com Wp Content Uploads 14 10 Quiz2av21annotatedak Pdf



Ecg A Pictorial Primer Medicine On Line Com




Lesson 4c Nuclear Cardiology Seminars



Rhythm Strip Ecg Guru Instructor Resources



Nclex Tutor Ekg Strips For The Nclex Beginners Youtube



Mark Hammerschmidt Arrythmia Faq



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography
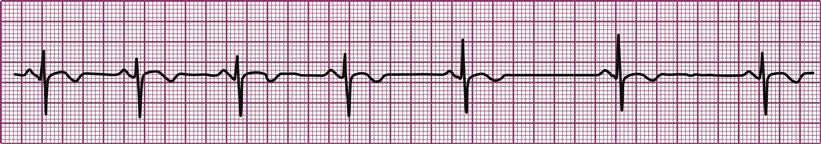



Cardiac Arrhythmias And Conduction Disturbances Musculoskeletal Key




Dysrhythmia Review Flashcards Quizlet




Patient No 3 A Rhythm Strip Shows Marked Sinus Bradycardia And Download Scientific Diagram



1




Section 11 Junctional Escape Rhythm
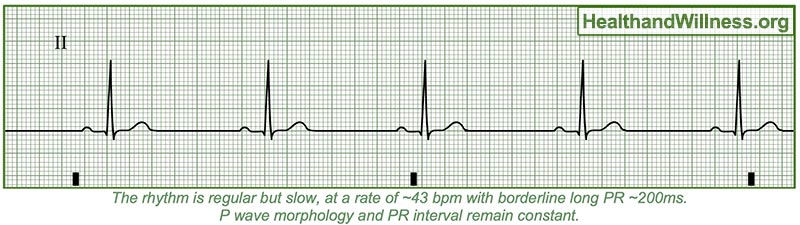



How To Read An Ekg Rhythm Strip Health And Willness
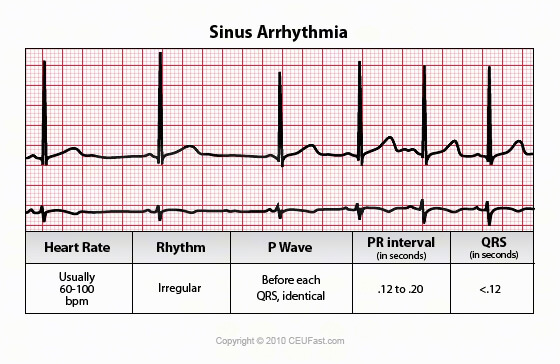



Ekg Ecg Interpretation Course Ceufast Nursing Continuing Education
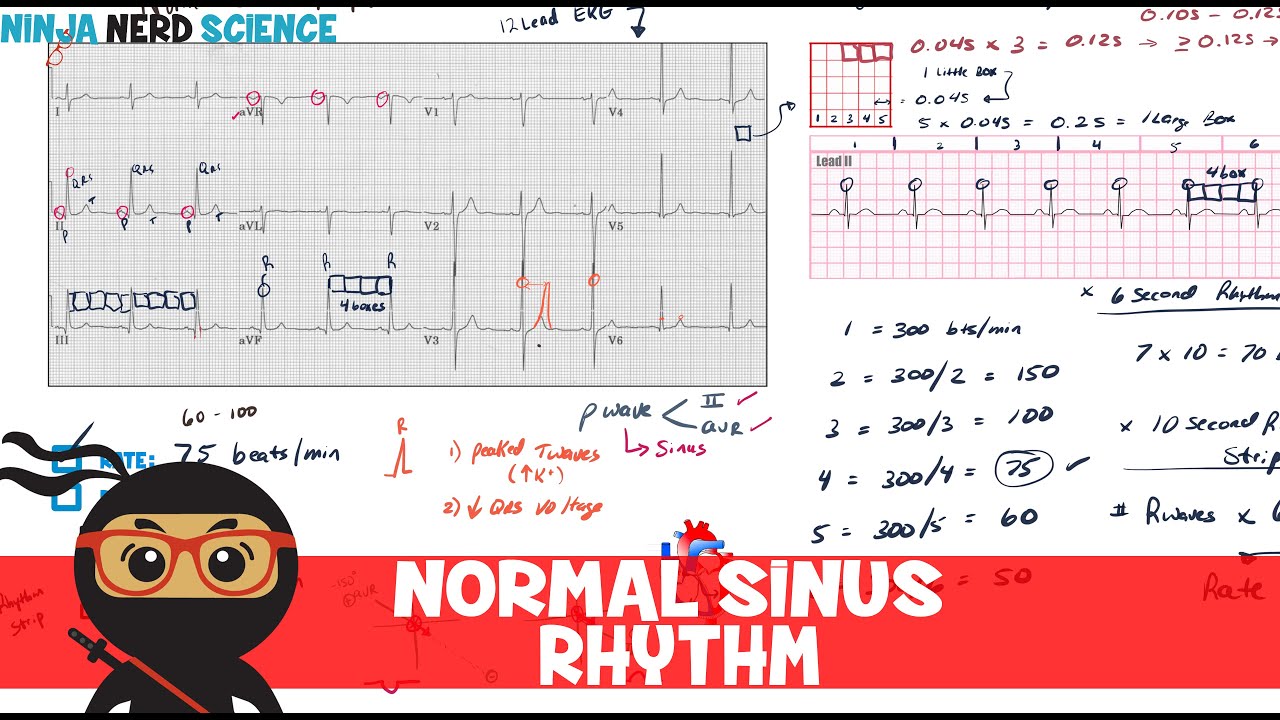



Rate And Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Youtube
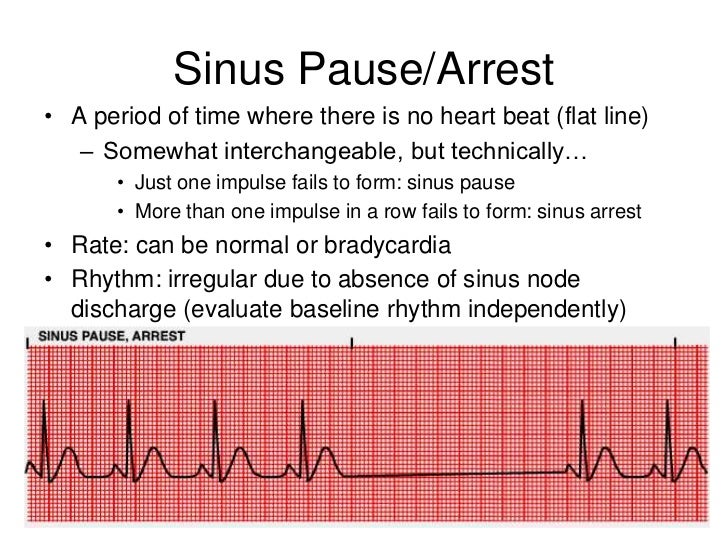



Basic Ekg And Rhythm Interpretation Symposia The Crudem Foundation



Www Bannerhealth Com Media Files Project Bh Careers Ekgguide Ashx



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf



Basic Rhythm Strip Review



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf



Http Www Bremss Org Uploadedfiles File Ekg Intermediate Tips Tricks Tools Pdf
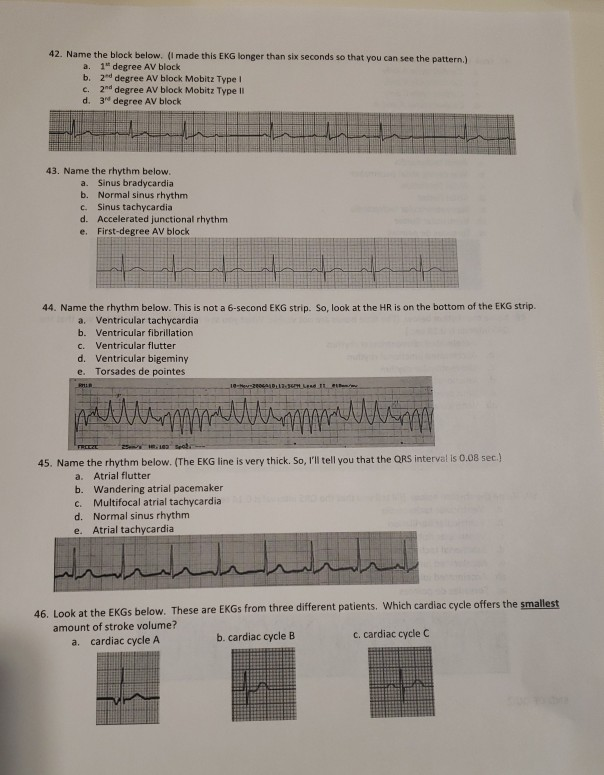



Solved 42 Name The Block Below I Made This Ekg Longer Chegg Com
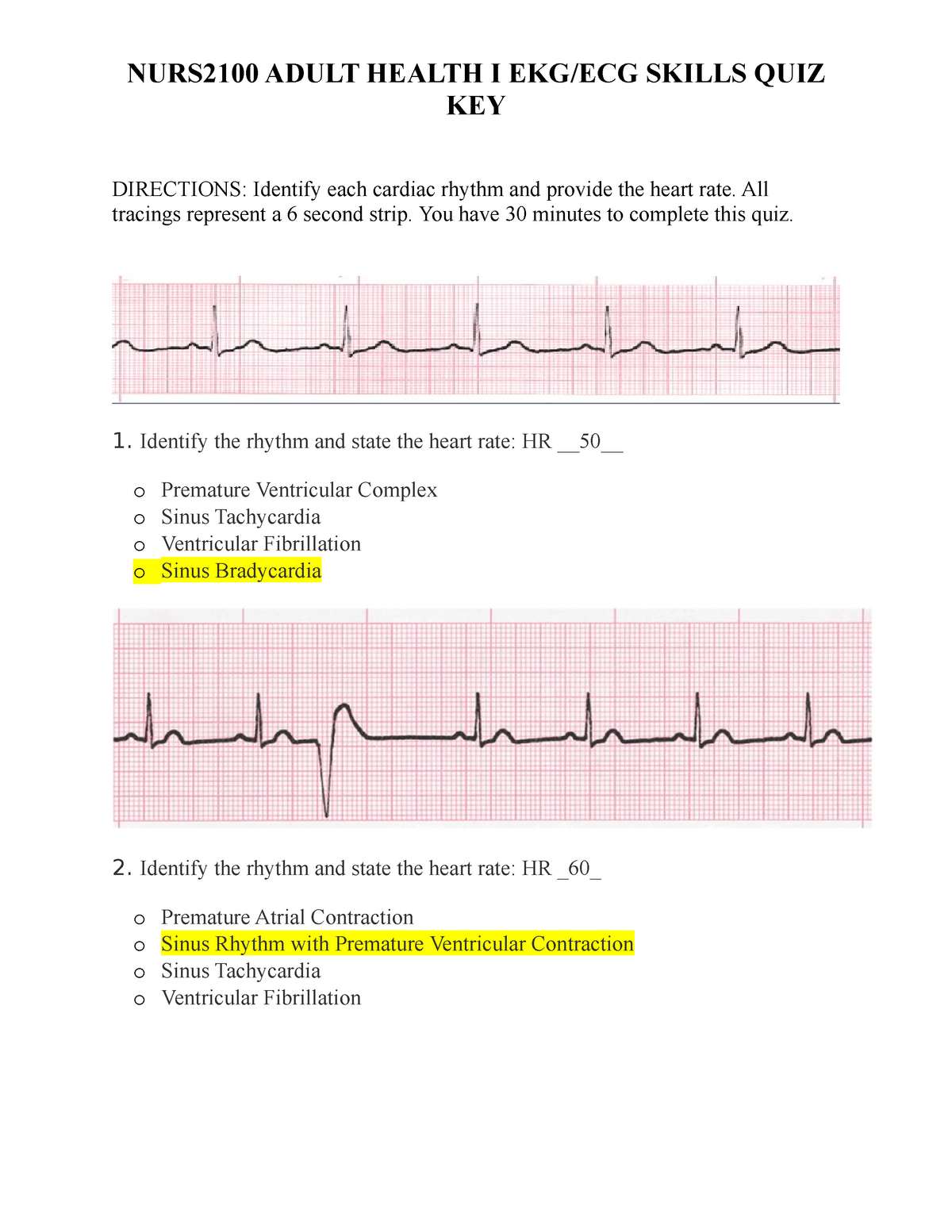



Sp19 Ekg Skills Quiz Ecg Ekg Simulation Lab Exercise Studocu




Ekg Normal Sinus Rythms Sinus Bradycardia More Leveluprn




Ekg Practice Test 1 Learn Master Acls Pals



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf
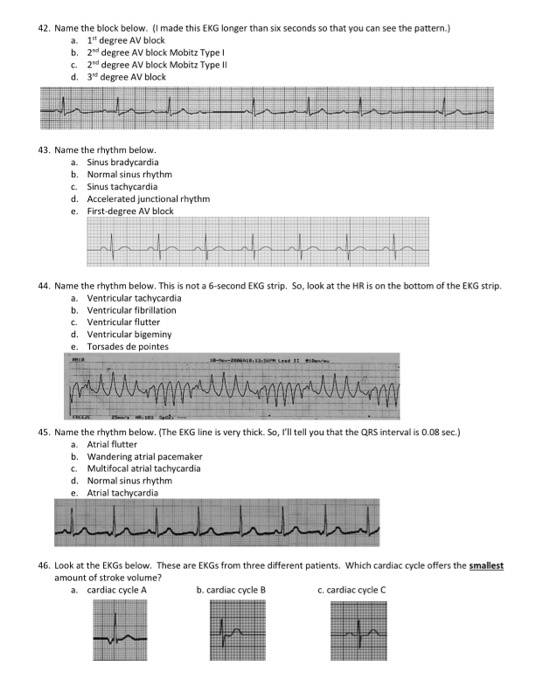



Made This Ename Block Mobits Typel Av Block Mobite Chegg Com
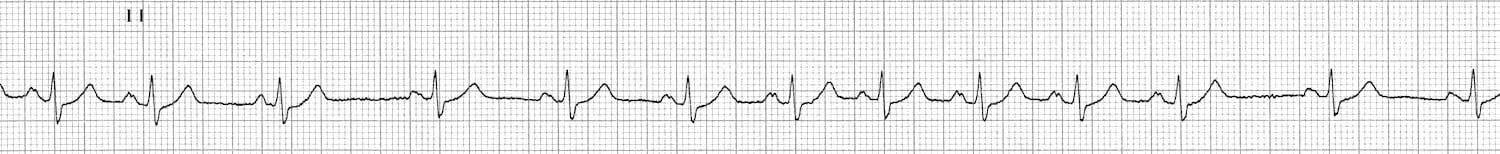



Sinus Arrhythmia Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics




Acls Symptomatic Bradycardia




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx



1



Www Skillstat Com Wp Content Uploads 14 10 Quiz2av21annotatedak Pdf



1



Www Skillstat Com Wp Content Uploads 14 10 Quiz2av21annotatedak Pdf



Rhythm Strip Flash Card Practice
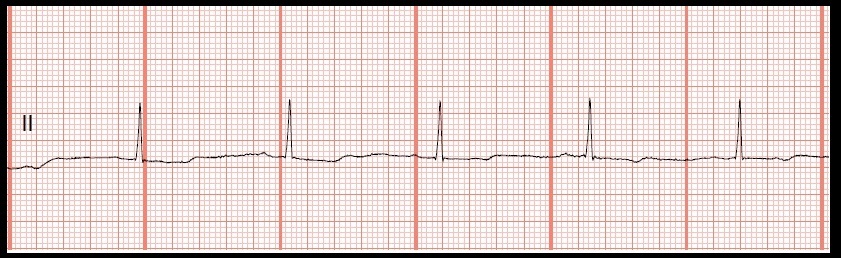



Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Strip Quiz 169




Cv Physiology Abnormal Rhythms Definitions




Start With The Rhythm Strip Ii




Evaluating And Managing Bradycardia Sciencedirect




Ekg Test 1 Internal Medicine Cardiovascular System
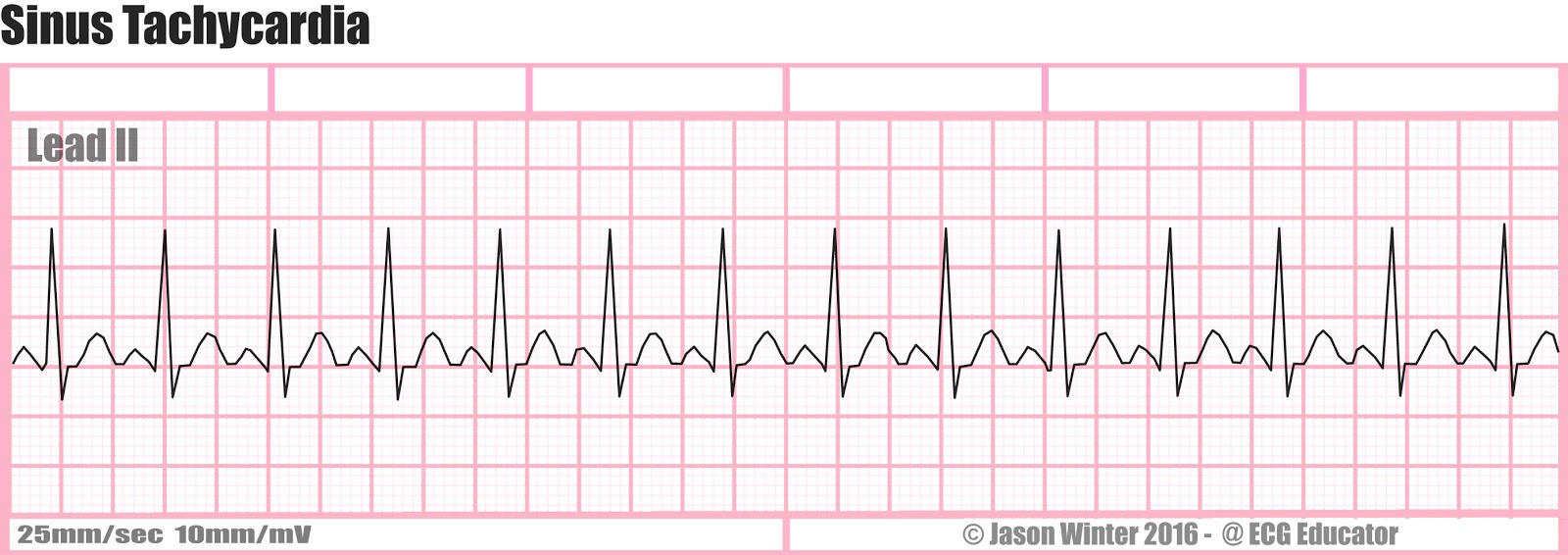



Ecg Educator Blog Six Second Ecg Rhythm Strips



Http Keymedinfo Com Site 667keym Cardiac Dysrhythmia Overview To Help With Acls Precourse Examination Pdf
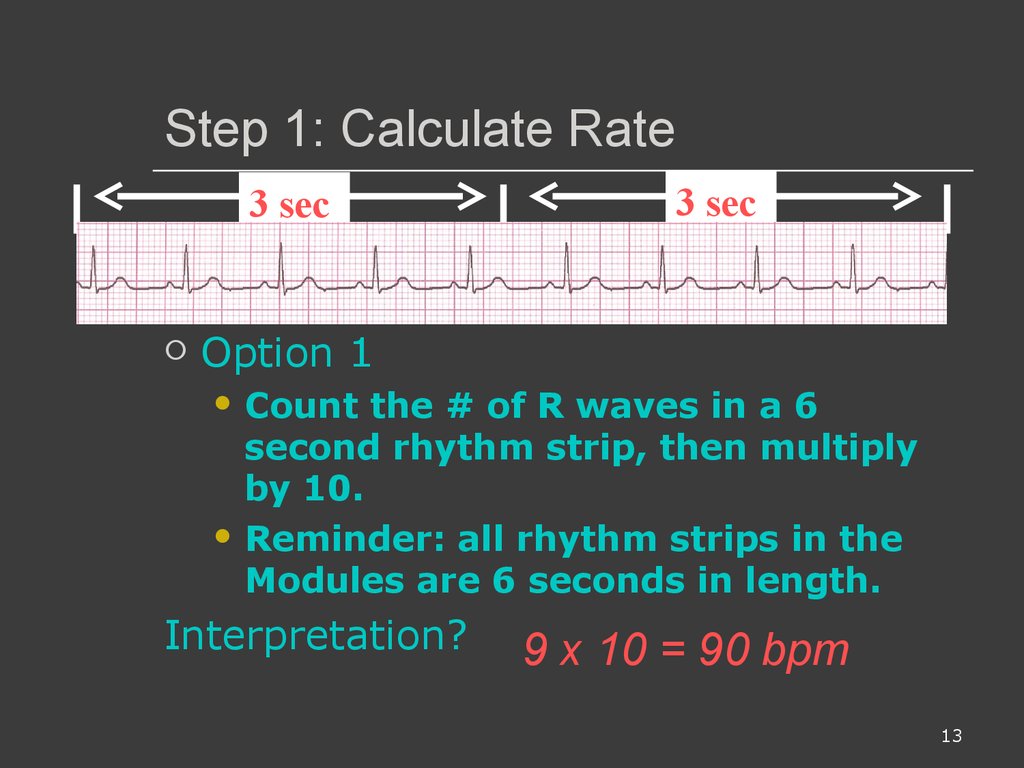



Ecg Interpretations How To Analyze A Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Heart Arrhythmias Diagnosing A Myocardial Infarction Prezentaciya Onlajn



Sinus Arrhythmia Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
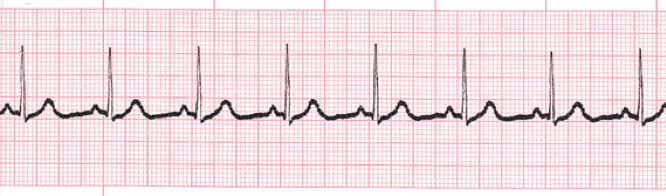



Normal Sinus Rhythm Training Acls Cardiac Rhythms Video Proacls




Sinus Rhythms Lessons Quiz




Sinus Bradycardia Wikipedia
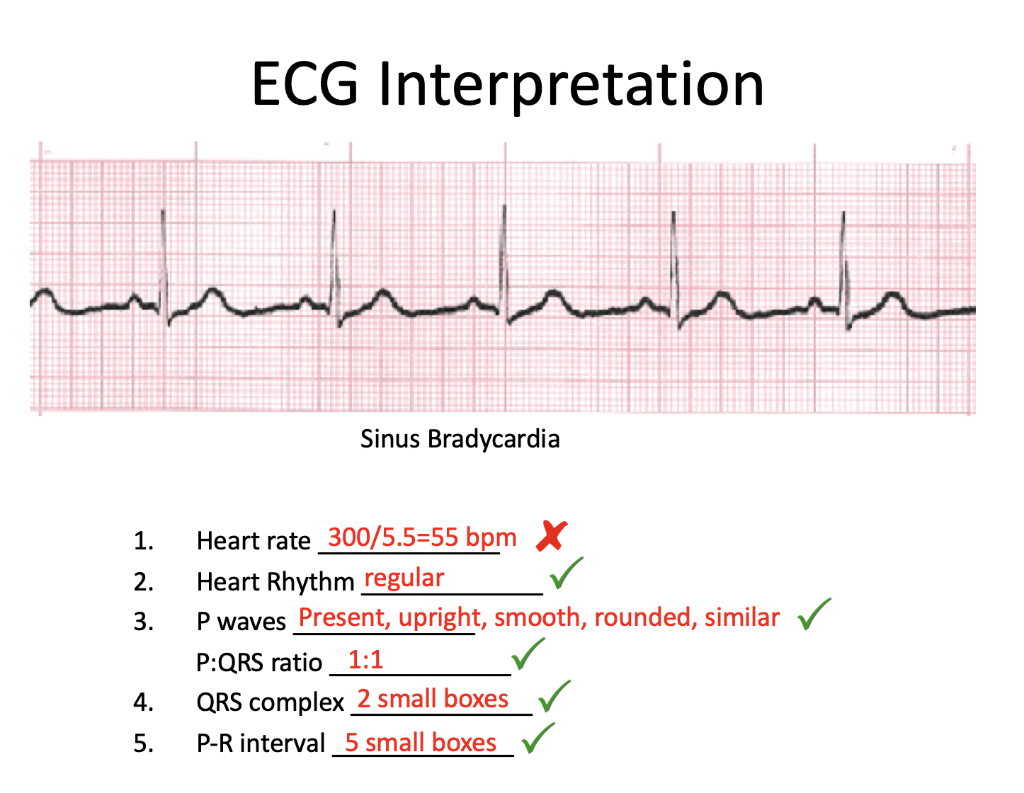



Ecg Interpretation رسیلیبریدہ س الم مراسم 1 2 3 Chegg Com




Sinus Bradycardia Wikipedia
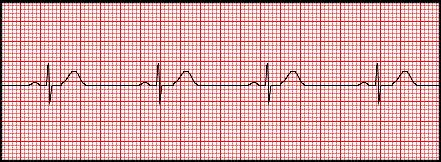



Ecg




Ecg Lead Ll Interpretation Answers 1 2 Nd
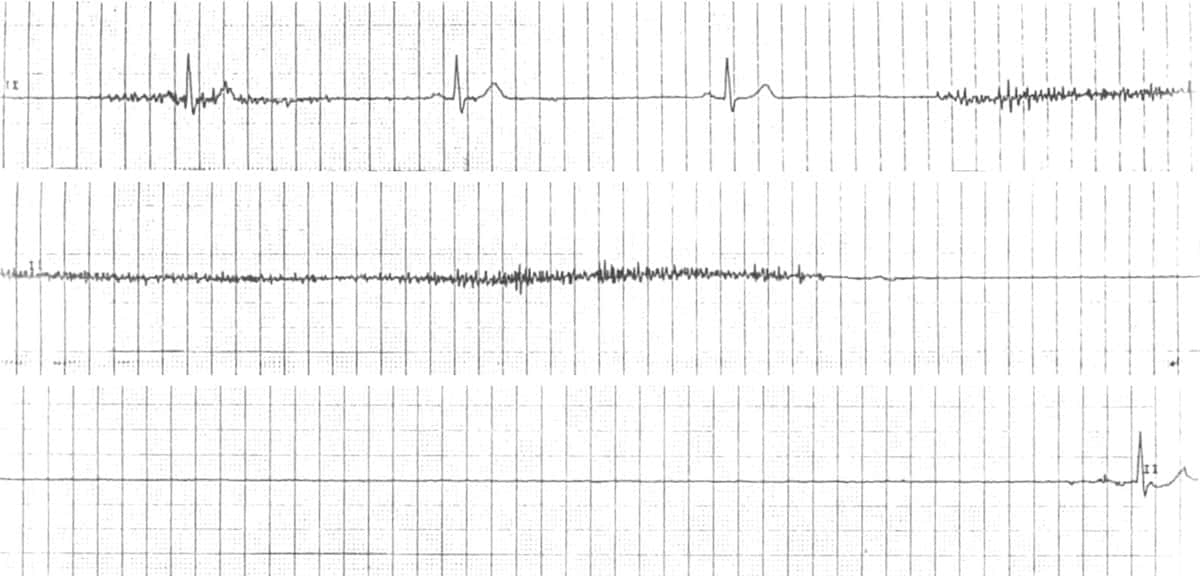



Sinus Node Dysfunction Sick Sinus Syndrome Litfl Ecg Library




How To Interpret Read Ekgs Like A Boss Master Heart Rhythms Education Nursejanx


コメント
コメントを投稿