コンプリート! paranasal sinuses x ray labeled 481856-Paranasal sinuses x ray anatomy
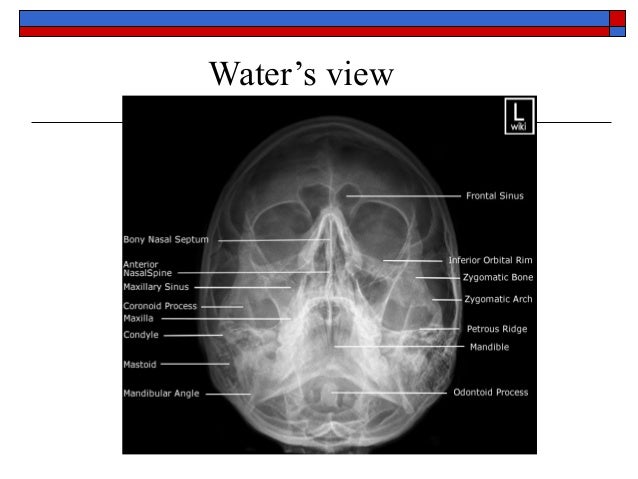
· Sinuses The aircontaining cavities situated in the frontal, ethmoidal, and sphenoidal bones of the cranium and the maxillary bones of the face are called the paranasal sinuses because of their formation from the nasal mucosa and their continued communication with the nasal fossae (Figs 221 and 222)Although the functions of the sinuses are not agreed on by all anatomists, · 2 Paranasal sinuses Water's view Caldwell view Lateral view Submentovertical view Right and left vertical view 3 Water's view Also called as occipitomental view or nosechin position In 1914,Dr CAWaters and CWWaldron,two British radiologists introduced this view Nose and chin touch the film and X ray beam is projected from occipital · Paranasal sinuses Maxillary sinus Sphenoid sinus 13 Positioning 14 PA 15 Caldwell Position Image 15 Occipito Mental OM (Waters) Position Image 16 Lateral View Position Image 17 RadiologicAnatomy 18 Plain Xray 19 Nasal Bones
Ent Radiology
Paranasal sinuses x ray anatomy
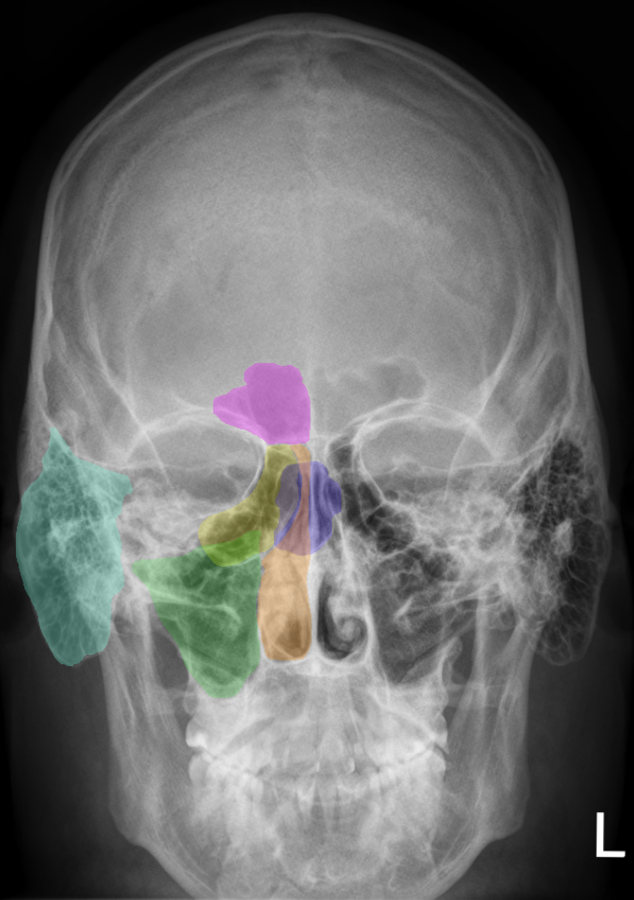
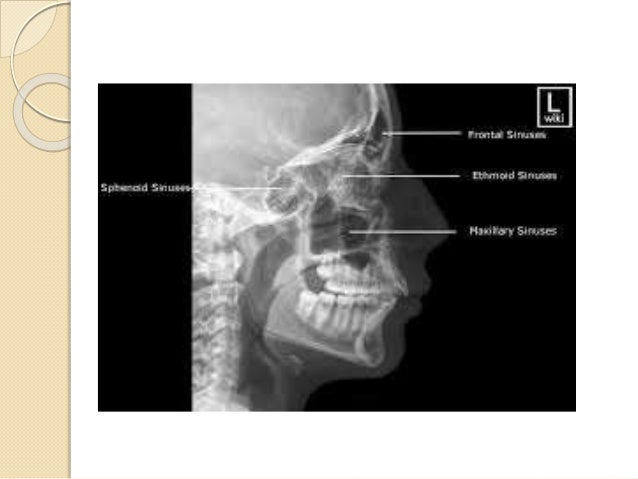
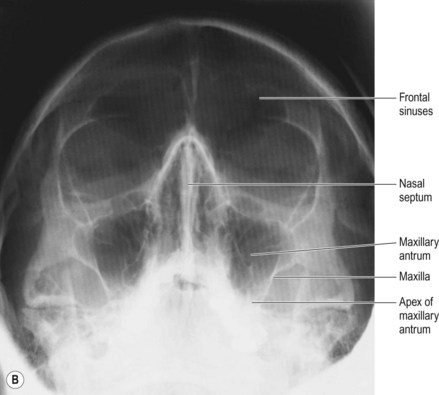
Paranasal sinuses x ray anatomy-Facial skeleton, paranasal sinuses;The ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes The sinuses are named for the facial bones in which they are located



Basic Anatomy Views Importance And Positioning Interpretation Skull
Paranasal sinuses is by plain Xray This should never be neglected since most nasa and paranasal l sinus pathology can be shown by this simple technique Virtually all expanding or bone eroding lesions in the sinuses can be recognized an, d in many instance as definitive diagnosis made, before resortin to more sophisticateg dAlgoritm for Ankle Fractures;Paranasal Sinuses Computed Tomography A computed tomography (CT) scan combines different Xray images from various angles around the body(8) It uses computer processing to produce crosssectional images or slices of the bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside the body
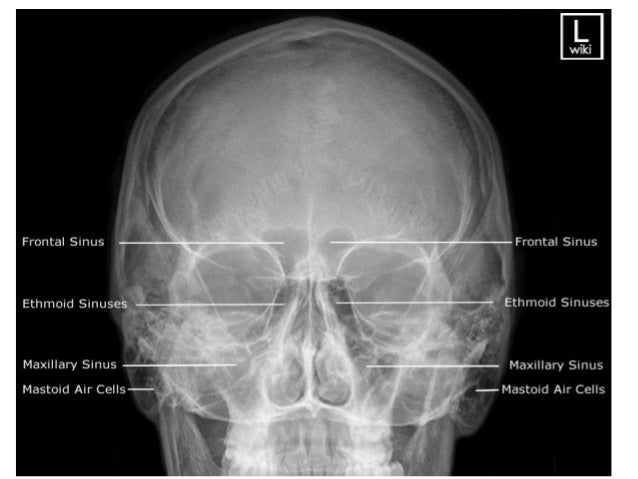
TIRADS TIRADS Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System;What are the paranasal sinuses a formation from from the nasal mucosa and their continued communication with the nasal fossae what is the best position to xray sinuses erect why do we xray sinuses erect air fluid levels when do paranasal sinuses start developing in the fetusSinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which may be due to infection, alle Labeled frontal sinus, ethmoid sinuses, maxillary sinus, nasal septum, eye socket
· Sinusitis is one of the most common diseases treated by primary care physicians Uncomplicated sinusitis does not require radiologic imagery However, when symptoms are recurrent or refractory0324 · The 4 paranasal sinuses include The frontal, maxillary, ethmoidal, and sphenoid sinuses Each of these sinuses have ducts that drain into the naso/oropharynx Frontal sinuses These are found between the outer and inner aspects of the frontal bone posterior to the superciliary arches, they are funnel shaped and they drain into the nasal cavity via theTinnitus Pulsatile and nonpulsatile tinnitus;




Waters View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Paranasal Sinuses Ct Anatomy W Radiology
The frontal sinuses are above the eyes;Xray paranasal sinuses were perform ed by Toshiba Xra y machine 03, unit m odeldrx3724 hd ma vol tage150 kvp Focal spot 12 /06 mm Waters' view examinati on wasIn an attempt to establish a standardized rating system for CT of the paranasal sinuses, the Committee on Rhinology and Paranasal Sinus Disease of the American Academy of OtolaryngologyHead and Neck Surgery instituted a protocol for the review of sinus CT scans at six international sites Fifty ide



Imaging Of Paranasal Sinuses




Radiographic Positioning Of The Paranasal Sinuses Youtube
The state, as well as most private health institutions have in their Arsenal of xray unit So go through the xray of the paranasal sinuses is not difficultLabeled frontal sinus, ethmoid sinuses, maxillary sinus, nasal septum, eye socket Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which may be due to infection, alle Front view illustration and sidebyside CT scans of normal and chronic sinusistis1305 · The paranasal sinuses are airfilled extensions of the nasal cavity There are four paired sinuses – named according to the bone in which they are located – maxillary, frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid Each sinus is lined by a ciliated pseudostratified epithelium, interspersed with mucussecreting goblet cells



Ent Radiology



Paranasal Sinuses X Ray Portal Myhealth
Xray CT data was approved by the institutional review board of Showa University 22 Physical nasal and paranasal tract model The 3D shape of the facial surface and the supraglottic airway including the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, and pharyngeal and laryngeal cavities was reconstructed from the Xray CT data · When it comes to imaging of neoplasms of the paranasal sinuses, CT and MRI play complementary roles It is not about the histology but about answering the question 'is it tumor or not?' and then determining the extent of the disease, for example intracranial or orbital extension Use MRI to differentiate inspissated secretions from neoplasmsHey, how you doing?Welcome to MedSchool Grammar, we are a team of students working to bring to you a one stop destination for concepts on RadiologyThis vide
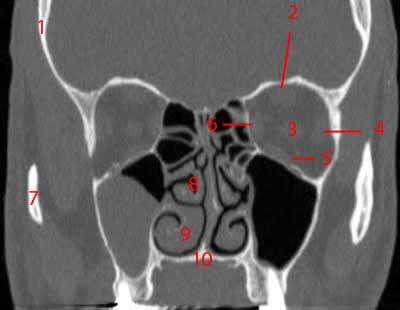



Paranasal Sinuses Ct Anatomy W Radiology



Www Mdpi Com 75 4418 11 2 250 Pdf
Radiography sinuses while delivering almost similar radiation doses when compared with standard 4 projection direct radiographs Plain radiography is generally obsolete, but exceptions include its use in confirming airfluid levels in acute sinusitis and in evaluating size and integrity of the paranasal sinuses RadiographsAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsCT sinus Indication/Technique Sinus CT is frequently requested by ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialists The CT test is usually made to evaluate the anatomy of the paranasal sinuses Information about the sinus anatomy of individual patients is essential prior to a FESS procedure (functional endoscopic sinus surgery)
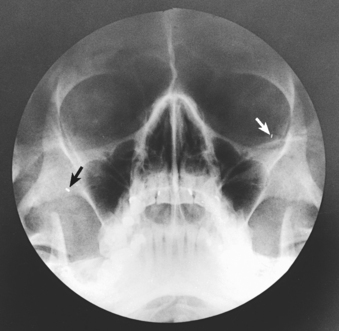



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
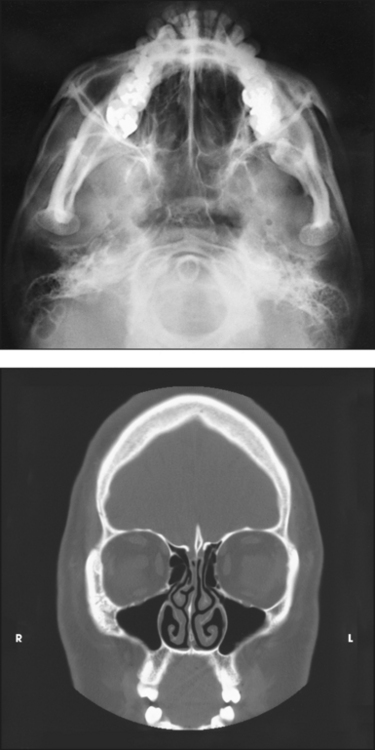



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
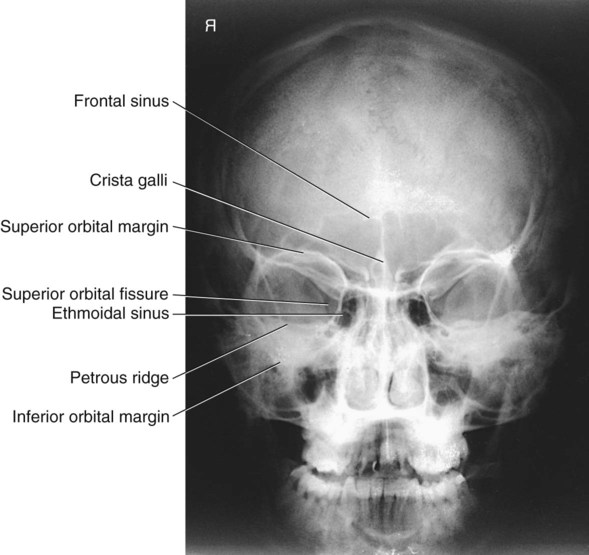
· Airfilled cavities located within specific facial and skull bones are known as paranasal sinuses 1 Humans have four paired paranasal sinuses, frontal, maxillary, sphenoid, and ethmoid, all extending from the respiratory area of the nasal cavity 2, and named after the bones they are found in Paranasal SinusesW530 AJR194, June 10 Hoang et al A C Fig 2—65yearold man undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery A, Labeled coronal CT image shows stages of procedure and anatomic variants of large right Haller cell (arrowhead), small left Haller cells, bilateral concha bullosa, and right concha lamella (asterisk)EB = ethmoidal bulla B, Endoscopic image of right nasal cavityA radiograph of a PA projection of the sinuses reveals that the petrous ridges are projected over the ethmoid sinuses Which of the following modifications will eliminate this superimposition while not compromising diagnostic quality?
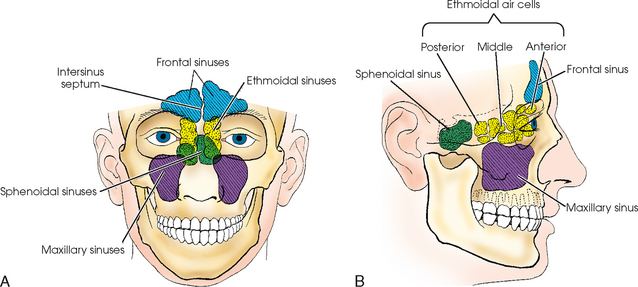



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key



Nose Anatomy And Histology Of The Human Nose Medical Library
MRI is useful for cases complicated by orbital or intracranial extension However, because of considerations of cost, the need for sedation, and for CT radiation exposure, conventional xray films will continue to play an important role in the diagnosis and management of medically treated sinus · Considerable progress in paranasal sinus imaging has occurred during the past decade as a result of refinements in computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) CT scanning has the ability to obtain thinslice, highresolution sectional imagesThis is an online quiz called Paranasal sinuses There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper Your Skills & Rank




Sinusitiserr



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
Head Radiography of the paranasal sinuses is performed to detect sinusitis (inflamama tion of the sinuses), as well as to detect fluid in the sinuses or polyps The examination is ordered when a patient experiences pain and pressure in the face, especially when lowering his or her head Radiography of the sinuses is an xray examination It may1305 · Skull Occipitomental Waters View Purpose and Structures Shown An angled PA view of the skull to evaluate for sinusitis and facial fracturesThe anatomy demonstrated includes the frontal and maxillary sinuses, inferior orbital rim, maxillae, zygoma, zygomatic arch (see radiographic positioning of the zygomatic arch), nasal septum, and floor of orbits1104 · The epithelial surface of the sinuses is an extension of the nasal mucosa Xray of the paranasal sinuses is done in the nasolabial, chin and axial projections, each of which is used to visualize a specific anatomical structure Sometimes additional stacking is applied, allowing to examine defects in more detail



Skull Facial Bones And Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key




The Canine Head And Skull Ct Atlas Of Veterinary Clinical And Radiological Anatomy Of The Dog
The paranasal sinuses usually consist of four paired airfilled spaces They have several functions of which reducing the weight of the head is the most important Other functions are air humidification and aiding in voice resonance They are named for the facial bones in which they are located maxillary sinus;Musculoskeletal Ankle Fracture mechanism and Radiography;A) Increase extension of the head and neck slightly B) Angle the CR 5° to 10° caudad



Frontal Sinus High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




21 Best Paranasal Sinuses Ideas Paranasal Sinuses Sinusitis Radiology
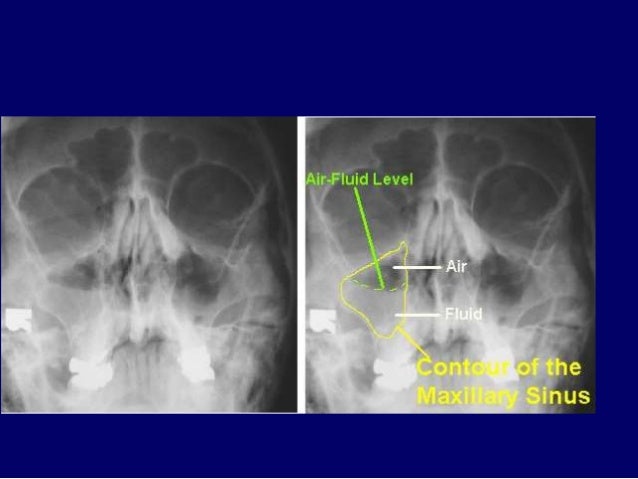
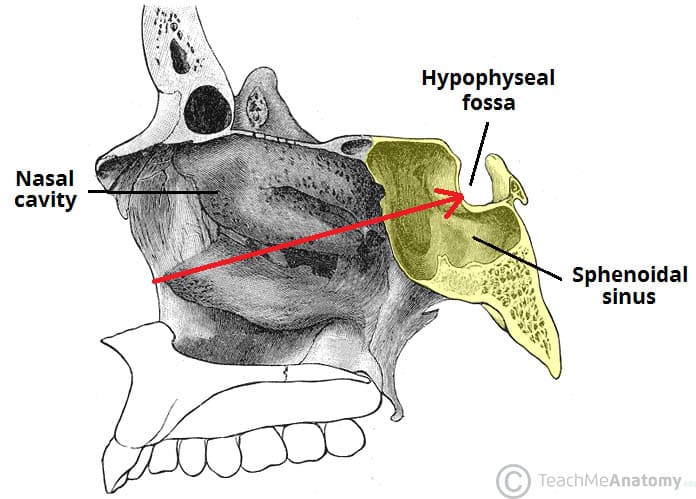
The ethmoid sinuses also called ethmoid labyrinth are located between the eyes and the nose Sinus in anatomy a hollow cavity recess or pocket In bones behind your nose are your sphenoid sinuses There are four pairs of paranasal sinuses the frontal sinuses are located above the eyes in the forehead bone The sphenoid sinuses areChild xray of the sinuses is performed only on strict indications suspected purulent process in the sinuses, traumatic injuries of facial bones Where better to do xrays?If on the other hand, the Xray beam is overhead and the patient prone or supine with the head turned to one side, the fluid will layer along the dependant wall of the sinus, and no airfluid level will be demonstrated The frontal sinuses are evaluated best in



Radiology Of Nose And Paranasal Sinuses



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
Paranasal sinuses and facial bones radiography Paranasal sinuses and facial bones radiography is the radiological investigation of the facial bones and paranasal sinuses Plain radiography of the facial bones is still often used in the setting of trauma, postoperative assessments and dental radiographyPoorly defined sella turcica that may indicate an abnormality of pituitary gland such as Sheehan syndrome and filling of sella turcica by CSF Can also be seen on xrays · When it comes to imaging of neoplasms of the paranasal sinuses, CT and MRI play complementary roles It is not about the histology but about answering the question 'is it tumor or not?' and then determining the extent of the disease, for example intracranial or orbital extension Use MRI to differentiate inspissated secretions from neoplasms



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy



Www Mdpi Com 75 4418 11 2 250 Pdf
1 Eur J Radiol 00 Mar;33(3)1852 Paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx CT and MRI Sievers KW(1), Greess H, Baum U, Dobritz M, Lenz M Author information (1)Radiology Associates Dortmund, Brüderweg 13, , Dortmund, Germany Neoplastic disease of the nose, paranasal sinuses, the nasopharynx and the parapharyngeal space requires thorough assessment ofLabeled Lateral Skull Radiographs What can you see here? · There are four principal modalities now used by the Radiologist to investigate the nose and paranasal sinuses These are plain Xray, conventional tomography, computerised tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance (MR) Plain Xray is the initial examination, and is used as a screening procedure before employing one of the tomographic techniques



Skull Facial Bones And Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key




Ct Anatomy Brain Anatomy Drawing Diagram
Weber and LaugeHansen ClassificationTemporal Bone Anatomy 10; · The PNS Xray is requested (2) when the patient experiences blocked sinuses due to too much of mucous build up, bacteria and germ which leads to infection and inflammation of the sinuses and is referred to as sinusitis (infection of the sinuses) Other sinuses related problems such as deviated septum Symptoms of other infection in the head area




Ent Radiology




Paranasal Sinuses Radigraphy Pns X Rays Waters View Youtube
· Learn about the anatomical appearances of the air sinuses of the skull as seen on CT images of the brain The frontal sinuses, sphenoid sinus, ethmoid air cells and mastoid air cells have very variable appearancesParanasal Sinuses MRI examination; · The four paired paranasal sinuses are the ethmoid, maxillary, frontal, and sphenoid sinuses These are named after the cranial bones in which they are located The sinuses normally contain air 6 6 TECHNIQUES OF SINUS EXAMINATION (1)PLAIN



Http Nu Edu Sa Documents 0 Atlas On X Ray And Angiographic Anatomy Pdf Ae6e9cde 4a53 4868 0a Ff7a344aead4




Caldwell View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Computed tomography (CT) of the sinuses uses special xray equipment to evaluate the paranasal sinus cavities – hollow, airfilled spaces within the bones of the face surrounding the nasal cavity CT scanning is painless, noninvasive and accurate It's also the most reliable imaging technique for determining if the sinuses are obstructed and · The paranasal sinuses are airfilled cavities within the ethmoid, frontal, and sphenoid bones and within the maxilla (Fig 175) They serve as resonating chambers for the voice and help to warm and moisten inhaled air The sinuses develop during childhood and are not fully formed until age 16 to 18Xrays and CT scan for diseases other than paranasal sinus lesions, and are accidentally found to have paranasal sinus lesion, were also included in this studyPatients who were presented to Department of Radiology with paranasal sinus lesions in past and were cured completely were excluded from the study
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/the-paranasal-sinuses/972PC0nYOzlz7wqSgLmNA_sinus_frontalis_large_u9Vfozc0uUoMtc6KtIaUfw.png)



Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
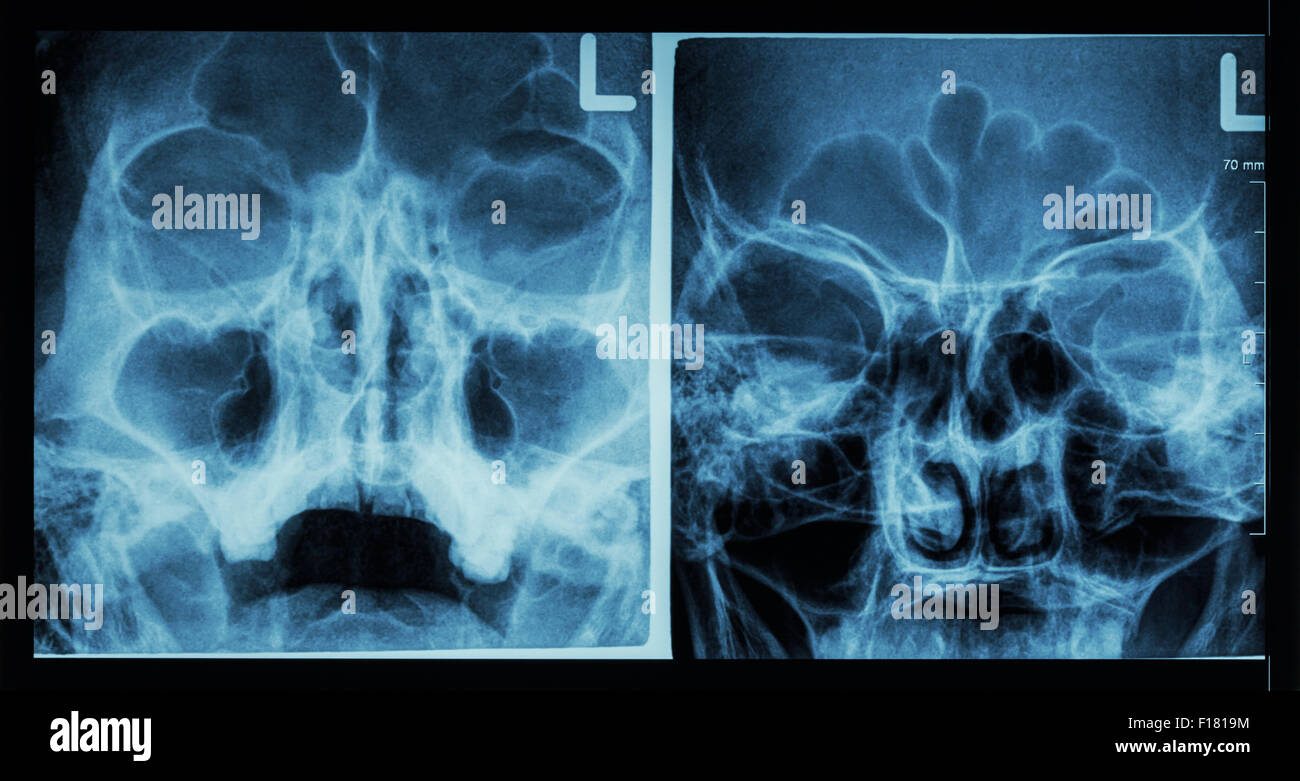



Ethmoid Sinus High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
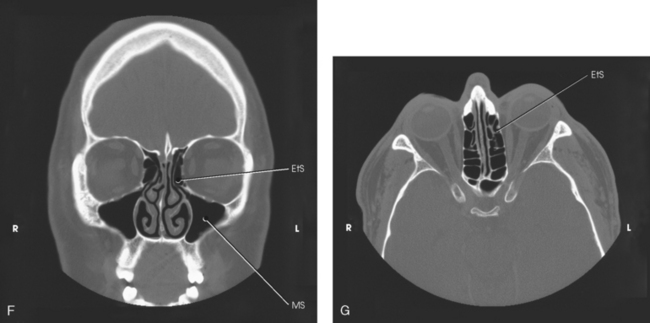
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired airfilled spaces that surround the nasal cavity The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes;Swallowing Swallowing disorders update;Distinctive regions within the nose and paranasal sinuses were delineated and labeled A to G for identification




Radiology Of The Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Ento Key
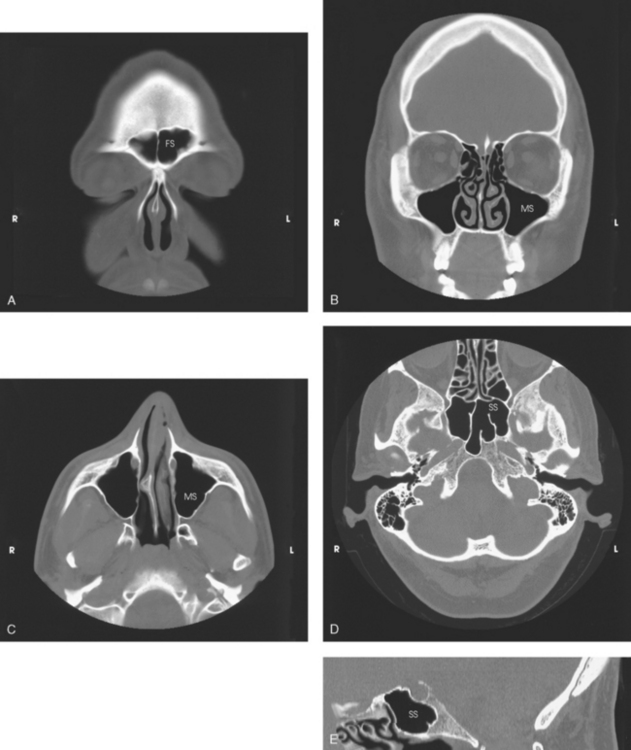



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key
0329 · A gray or white area on an Xray of the sinuses indicates a problem This is most often due to inflammation or a buildup of fluid in the sinuses A sinus Xray may also be called Xray
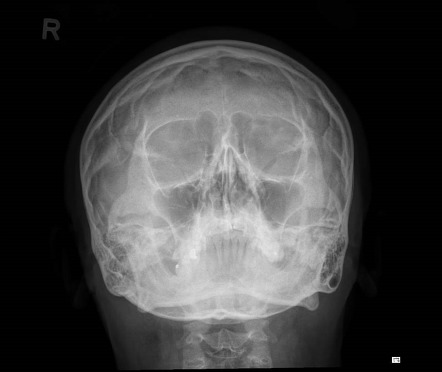



Waters View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
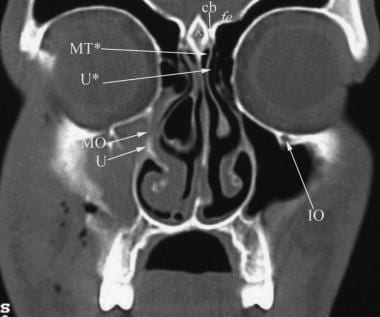



Ct Scan Of The Paranasal Sinuses History Basic Concepts Anatomy
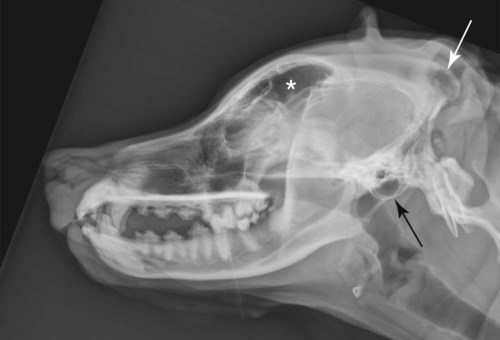



The Cranial And Nasal Cavities Canine And Feline Veterian Key




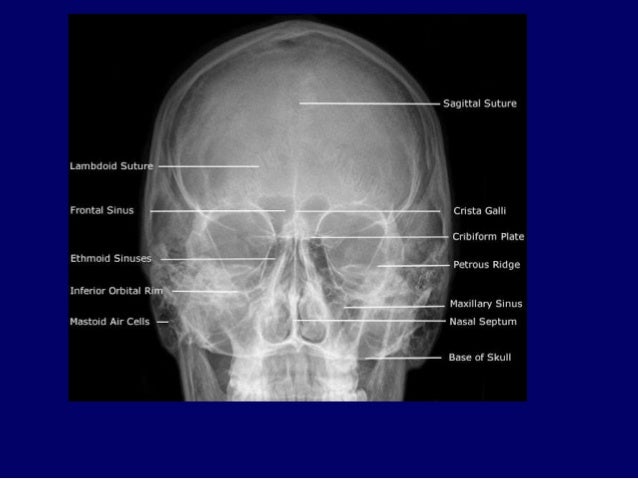
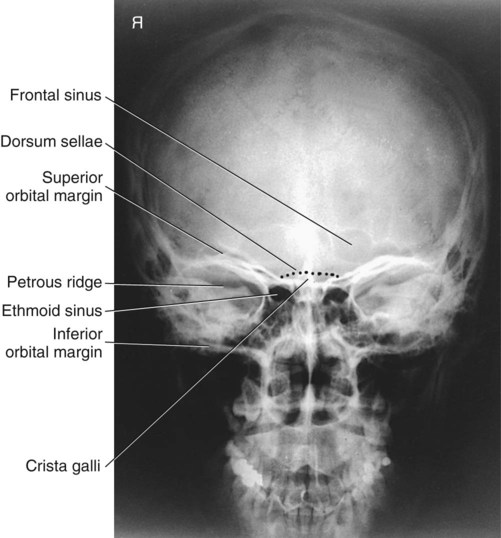
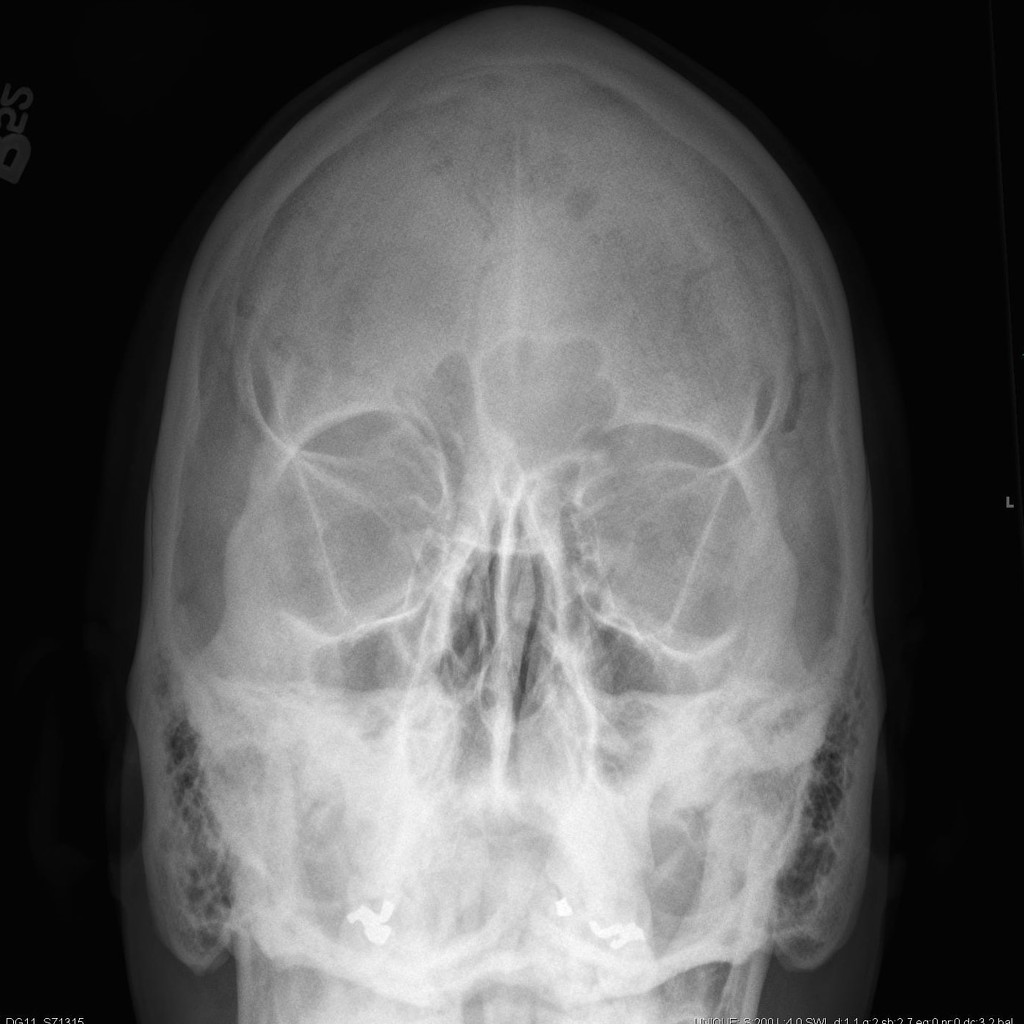
Identify On A P Head X Ray 1 Frontal Sinus 2 Ethmoid Air Cells 3 Maxillary Sinus 4 Nasal Septum 5 Crista Galli 6 Inferior Nasal Concha 7 Coronoid Process Ppt Download




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia



Sinusitis Mastoiditis Undergraduate Diagnostic Imaging Fundamentals




Pin On X Ray
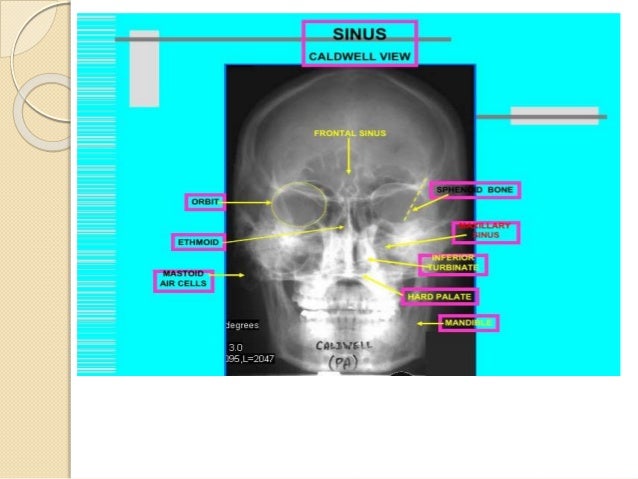



Radiology Of Nose And Paranasal Sinuses



Http Nu Edu Sa Documents 0 Atlas On X Ray And Angiographic Anatomy Pdf Ae6e9cde 4a53 4868 0a Ff7a344aead4



Paranasal Sinuses X Ray Portal Myhealth
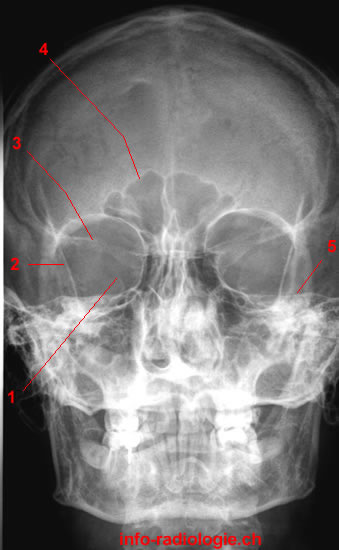



Paranasal Sinuses Radiography W Radiology




Pdf Magnetic Resonance Imaging Computed Tomography And Cross Sectional Views Of The Anatomy Of Normal Nasal Cavities And Paranasal Sinuses In Mesaticephalic Dogs
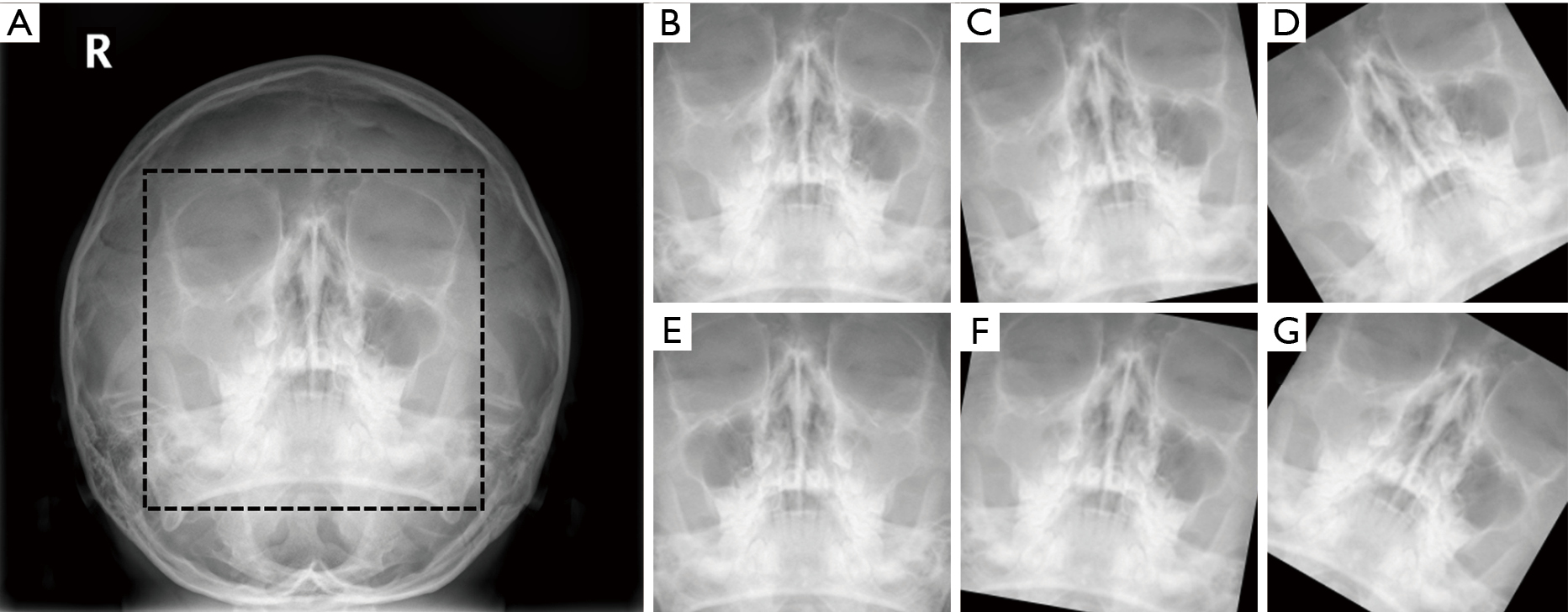



Improvement Diagnostic Accuracy Of Sinusitis Recognition In Paranasal Sinus X Ray Using Multiple Deep Learning Models Kim Quantitative Imaging In Medicine And Surgery




21 Best Paranasal Sinuses Ideas Paranasal Sinuses Sinusitis Radiology




Computed Tomography Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses And Anatomical Variants Of Clinical Relevants In Nigerian Adults Sciencedirect




Small Animal Skull Nasofacial Radiography Including The Nasal Cavity Frontal Sinuses Today S Veterinary Practice




Small Animal Skull Nasofacial Radiography Including The Nasal Cavity Frontal Sinuses Today S Veterinary Practice




Orbits Anatomy Mri Orbits And Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Free Cross Sectional Anatomy




X Ray Of The Para Nasal Sinuses Showing Increased Softtissue Density Download Scientific Diagram



1
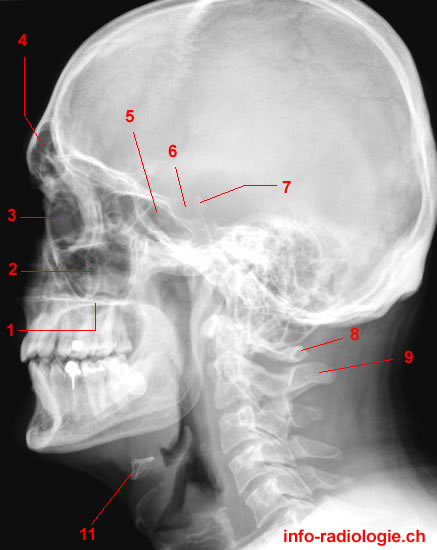



Paranasal Sinuses Radiography W Radiology
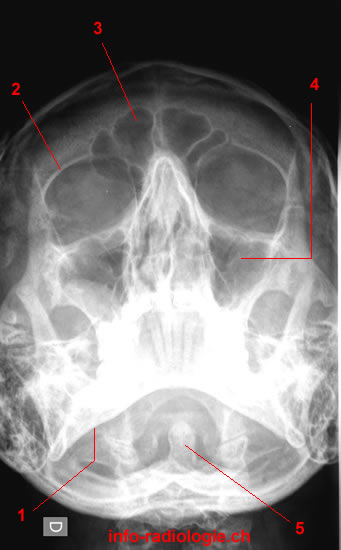



Paranasal Sinuses Radiography W Radiology




Paranasal Sinuses And Facial Bones Radiography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
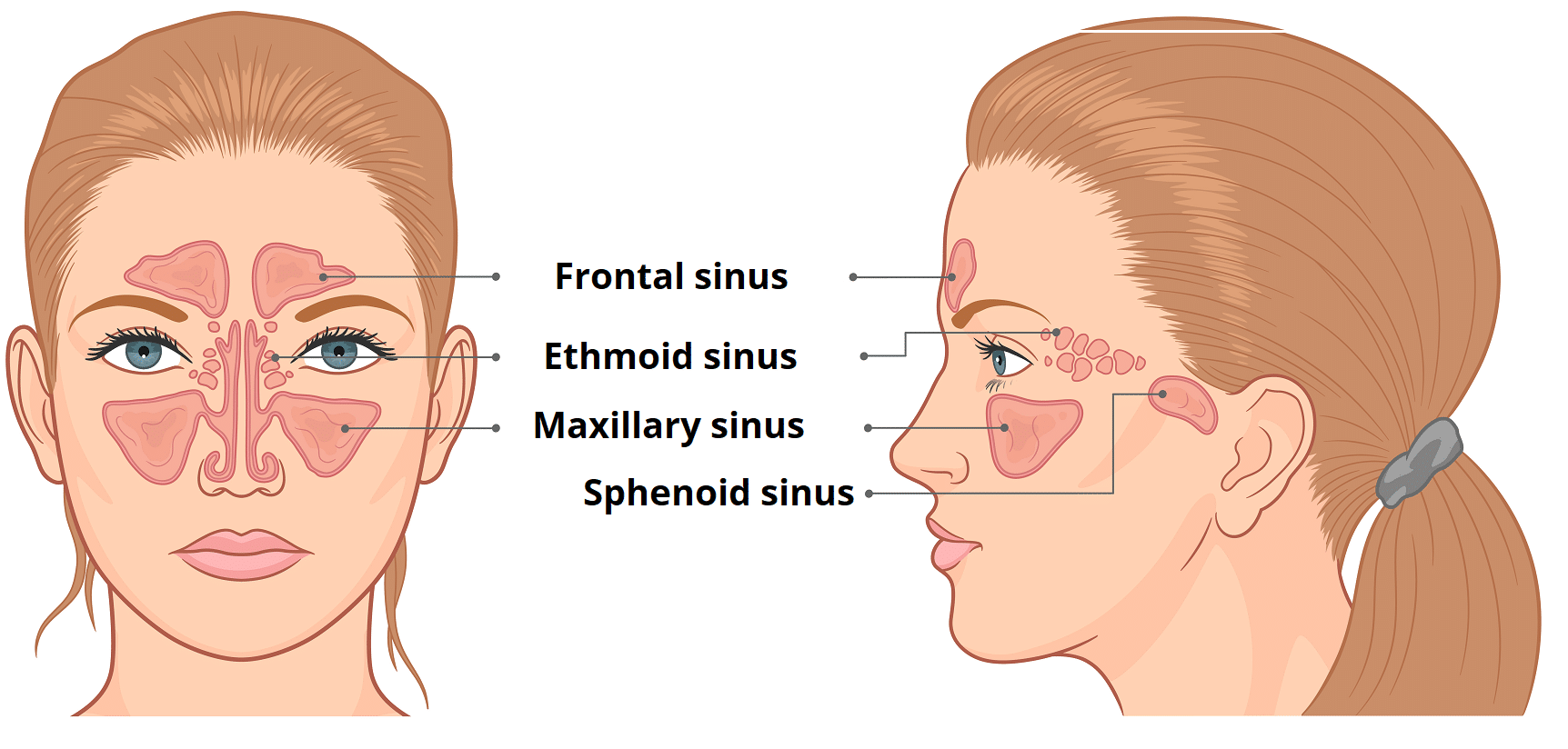



The Paranasal Sinuses Structure Function Teachmeanatomy
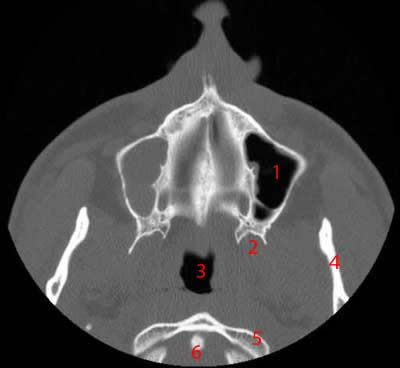



Paranasal Sinuses Ct Anatomy W Radiology
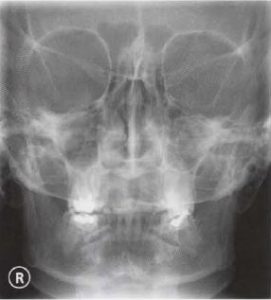



Ce4rt Radiographic Positioning Face And Mandible For X Ray Techs




Maxillary Sinusitis Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
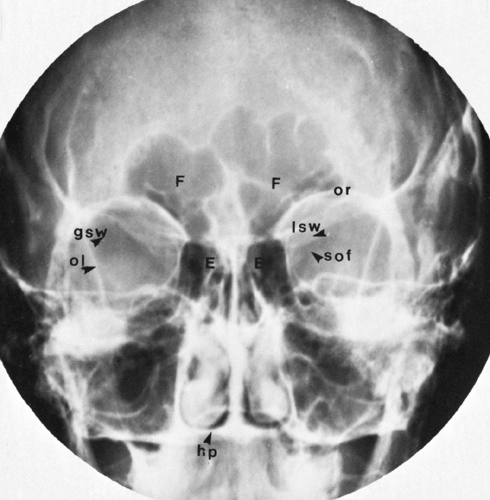



The Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key



Paranasal Sinuses And Facial Bones Radiography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
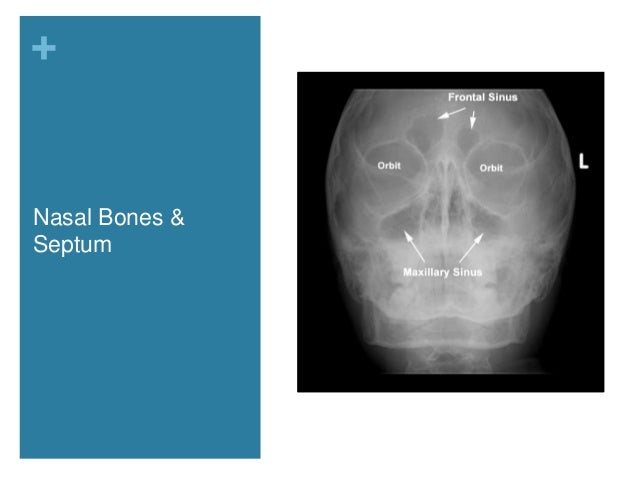



Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Radiologic Anatomy



Performance Of Deep Learning To Detect Mastoiditis Using Multiple Conventional Radiographs Of Mastoid



1




Basic Anatomy Views Importance And Positioning Interpretation Skull



Paranasal Sinuses X Ray Anatomy Tondahtyuimcfall



Http Nu Edu Sa Documents 0 Atlas On X Ray And Angiographic Anatomy Pdf Ae6e9cde 4a53 4868 0a Ff7a344aead4



1




Oral And Maxillofacial Anatomy Radiologic Clinics




Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
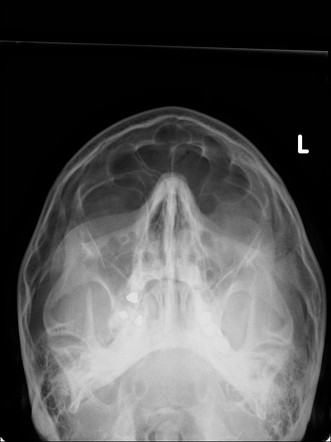



Paranasal Sinuses And Facial Bones Radiography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




Paranasal Sinus Definition Location Anatomy Function Picture




Radiology Of The Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Ento Key




Transverse Computed Tomography Image Of The Head Warmblood Stallion Download Scientific Diagram



Plain Film X Ray Principles Interpretation Teachmeanatomy



Home Page



Feline Head Imaging Continuity With Practitioner And Radiology Vetbloom Blog




21 Best Paranasal Sinuses Ideas Paranasal Sinuses Sinusitis Radiology




Paranasal Sinuses And Facial Bones Lateral View Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org



Caldwell View Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
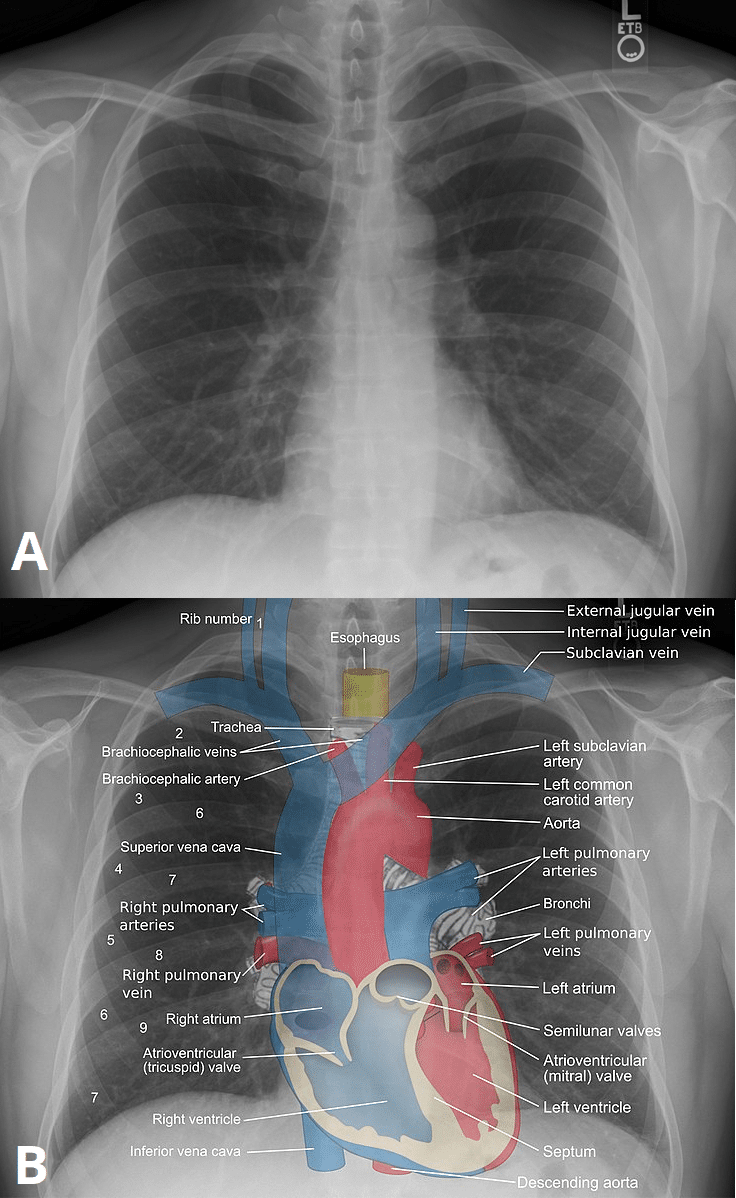
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12296/chest_PA.jpg)



Radiological Anatomy X Ray Ct Mri Kenhub
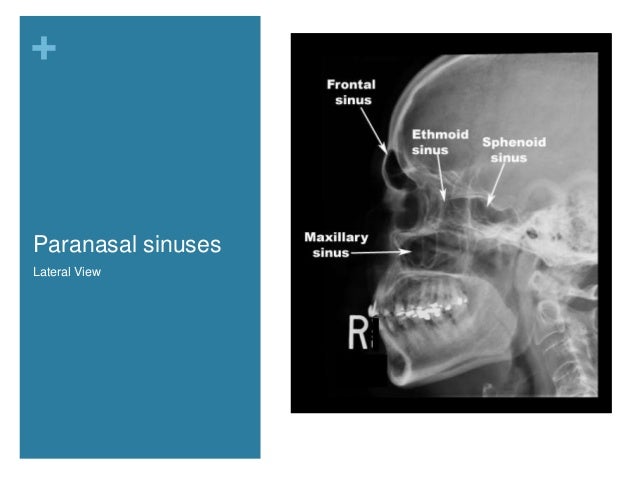



Nasal Cavity And Paranasal Sinuses Radiologic Anatomy




Paranasal Sinuses Wikipedia




Paranasal Sinuses Maxillary Ethmoid Sphenoid Frontal Notes Youtube




Paranasal Sinus Anatomy What The Surgeon Needs To Know Intechopen




Paranasal Sinuses And Facial Bones Radiography Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
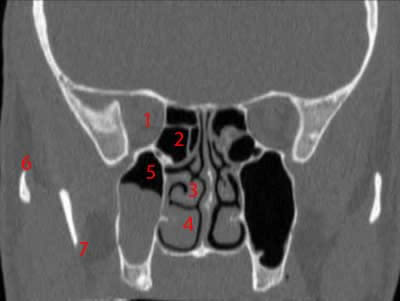



Paranasal Sinuses Ct Anatomy W Radiology



Postnasal Drip Syndrome I Sinusitis Imaging
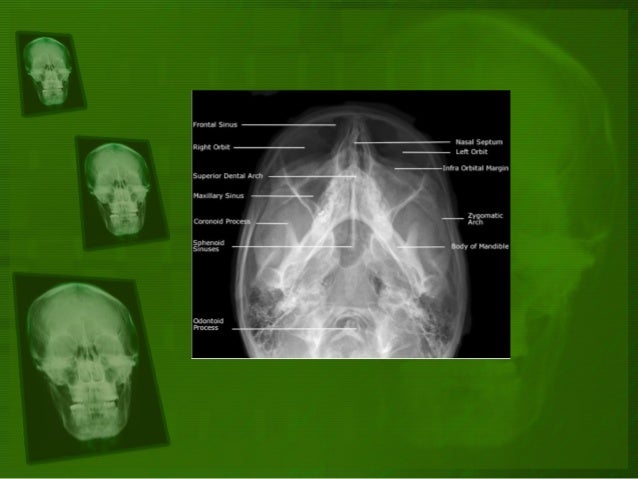



Positioning And Radiographic Anatomy Of The Skull




Computed Tomography Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses And Anatomical Variants Of Clinical Relevants In Nigerian Adults Sciencedirect



Http Nu Edu Sa Documents 0 Atlas On X Ray And Angiographic Anatomy Pdf Ae6e9cde 4a53 4868 0a Ff7a344aead4




Computed Tomography Anatomy Of The Paranasal Sinuses And Anatomical Variants Of Clinical Relevants In Nigerian Adults Sciencedirect
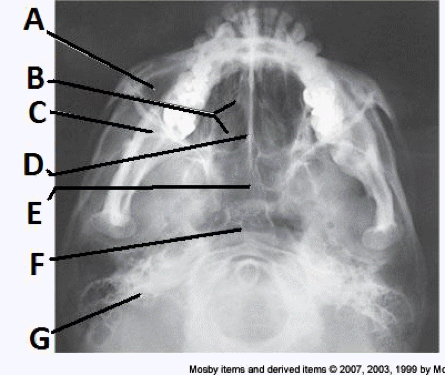



Final Flashcards Easy Notecards




Identify On A P Head X Ray 1 Frontal Sinus 2 Ethmoid Air Cells 3 Maxillary Sinus 4 Nasal Septum 5 Crista Galli 6 Inferior Nasal Concha 7 Coronoid Process Ppt Download
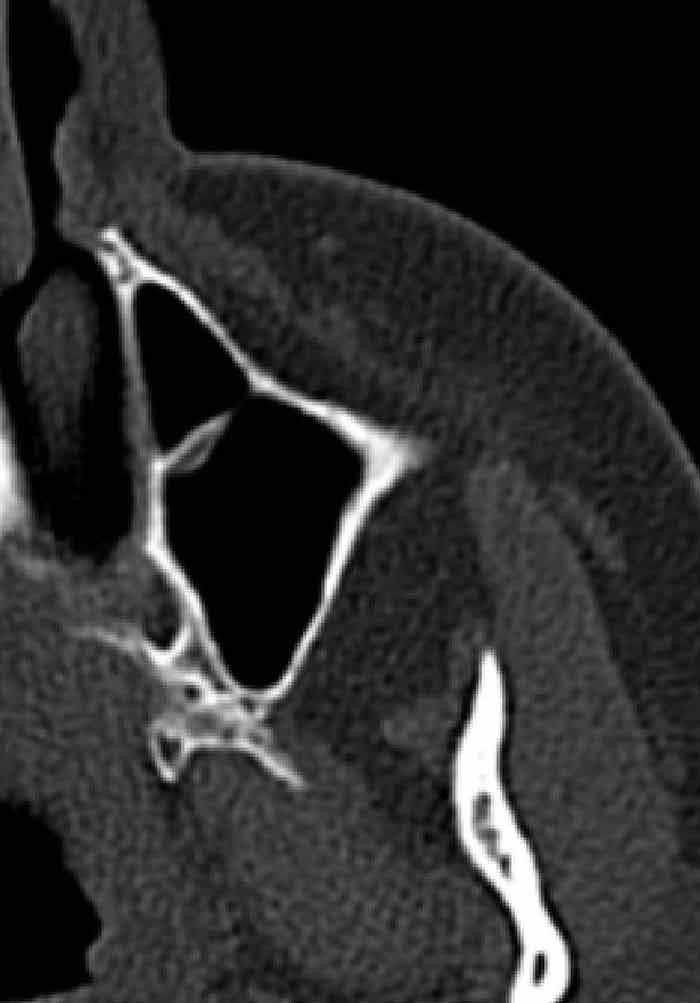



Paranasal Sinus Anatomy What The Surgeon Needs To Know Intechopen




Sinusitiserr




Startradiology




Startradiology



1
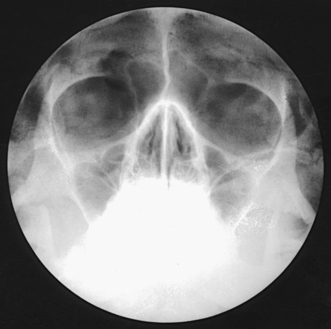



Paranasal Sinuses Radiology Key




Paranasal Sinus Anatomy What The Surgeon Needs To Know Intechopen
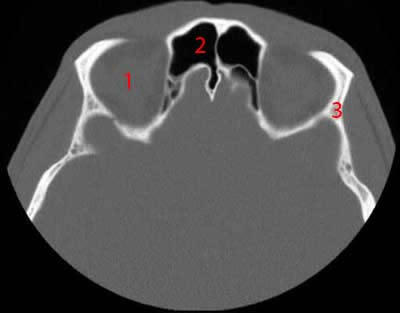



Paranasal Sinuses Ct Anatomy W Radiology




Orbits Anatomy Mri Orbits And Paranasal Sinuses Anatomy Free Cross Sectional Anatomy
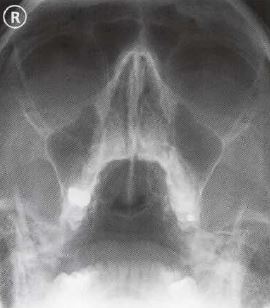



Ce4rt Radiographic Positioning Face And Mandible For X Ray Techs


コメント
コメントを投稿